This project aims to optimize the design of the catalytic cracking downer reactor using a hybrid model of machine learning and computational particle fluid dynamics. The preliminary fluid dynamic model will be validated in several lab-scale units already developed in KAUST, and the data generated by the validated model and experiments will be used by machine learning algorithms to infer optimized geometries, designs, and prototypes based on a set of constraints and boundaries. Different machine learning approaches will be applied and optimized for the aim of developing a hybrid model as a tool of process and technology improvement.
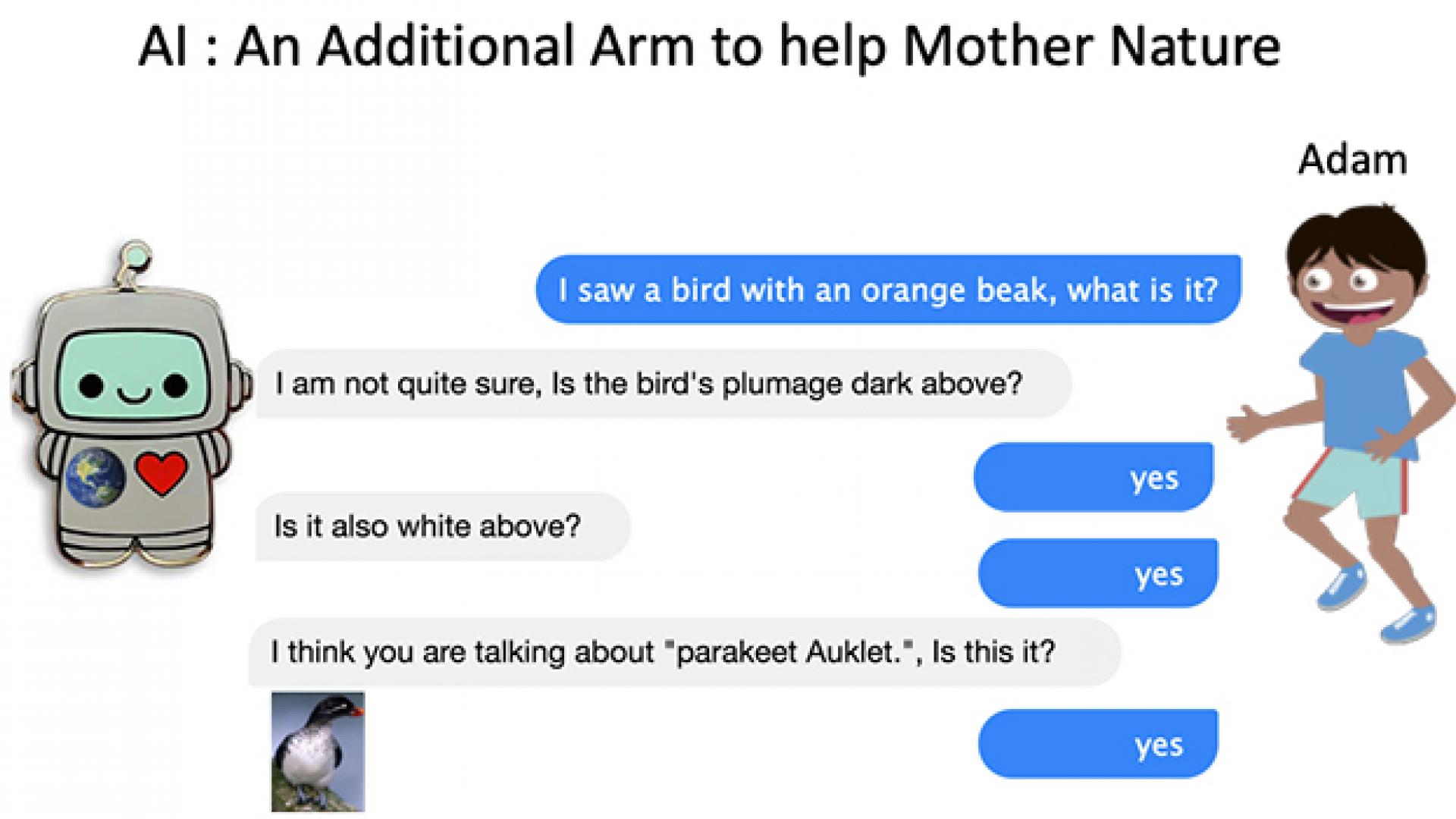
By training a search agent to make smarter exploratory decisions, relational data can be classified more accurately and efficiently.
The psychology of human creativity helps artificial intelligence imagine the unseen.