Nowadays, integrated circuits (IC) are mostly implemented using Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) transistor technology. This technology has allowed the chip industry to shrink the transistors and thus increase the device density, complexity, operation speed, and computation power of the ICs. However, in recent years, the transistor scaling has faced multiple roadblocks, which will eventually lead the scaling to an end due to approaching the fundamental physical limits.
The dominance of sub-threshold leakage, which slows down the scaling of threshold voltage VTH and the supply voltage VDD has resulted in high power density on the chips, and even widely popular solutions such as parallel and multi-core computing have not been able to address that problem adequately.
All of these drawbacks have overshadowed the benefits of transistor scaling. With the dawn of the Internet of Things (IoT) era, the chip industry needs adjustments towards ultra-low-power circuits and systems.
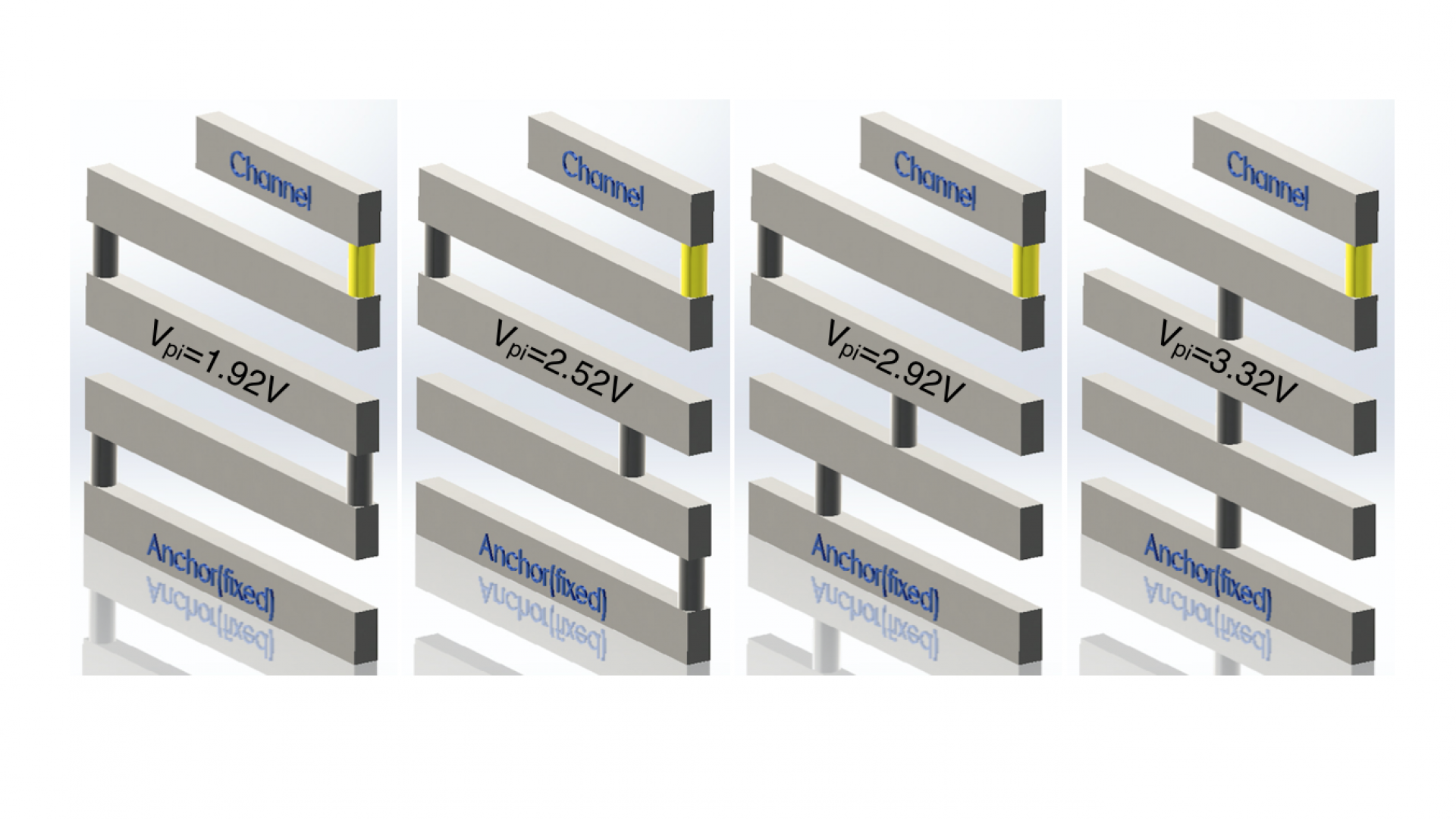
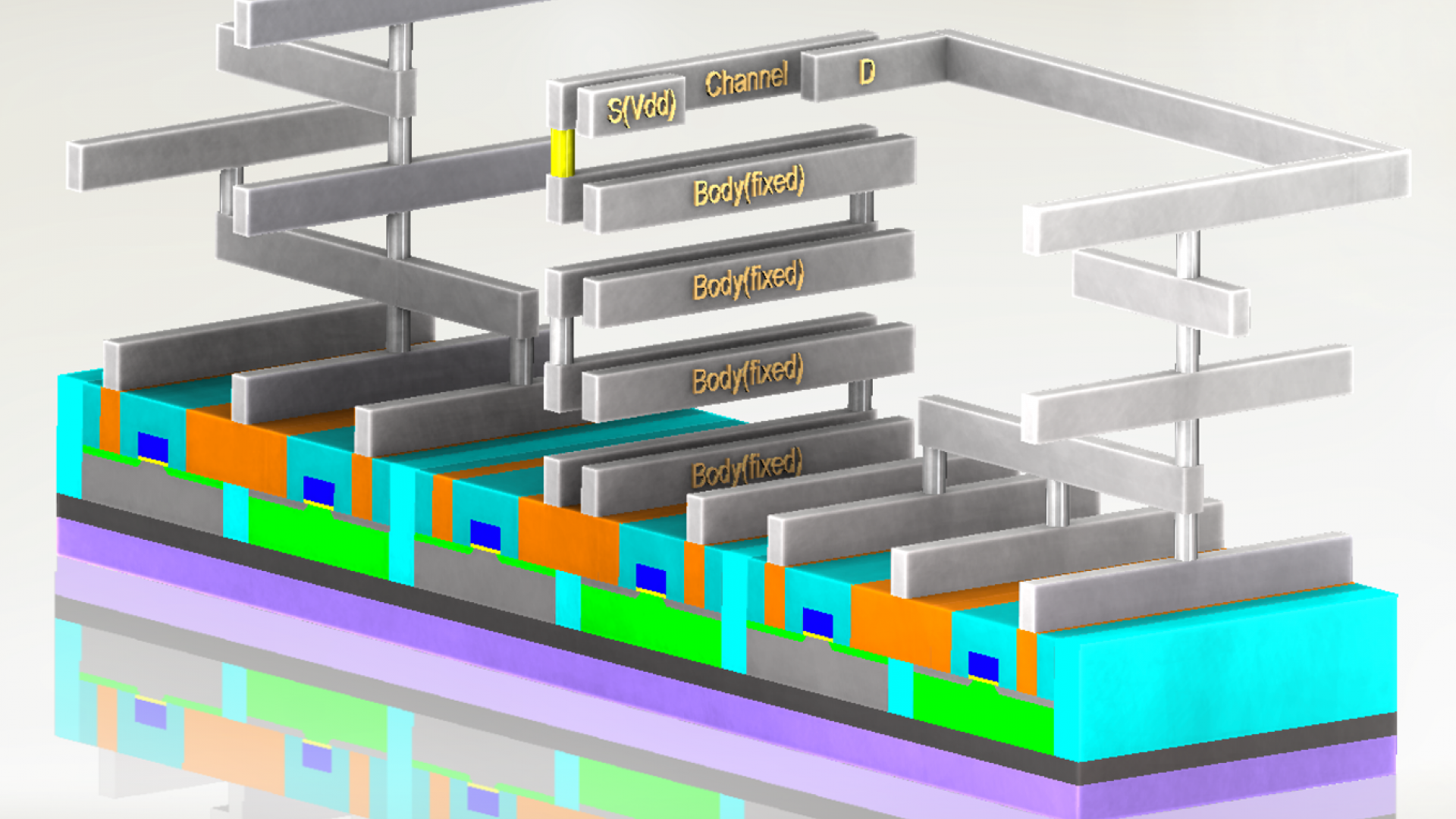
Energy-efficient NEM relay provides an alternative way of ultra-low power computation. With its zero sub-threshold leakage property and sharp turn on/off curves, essential applications in integrated circuit and system can be built with BEOL NEM relays. To name a few, we have design and proposed below applications implemented by all NEM relays:
- Relay logics, which use relays in logic gates by utilizing their unique switching characteristics
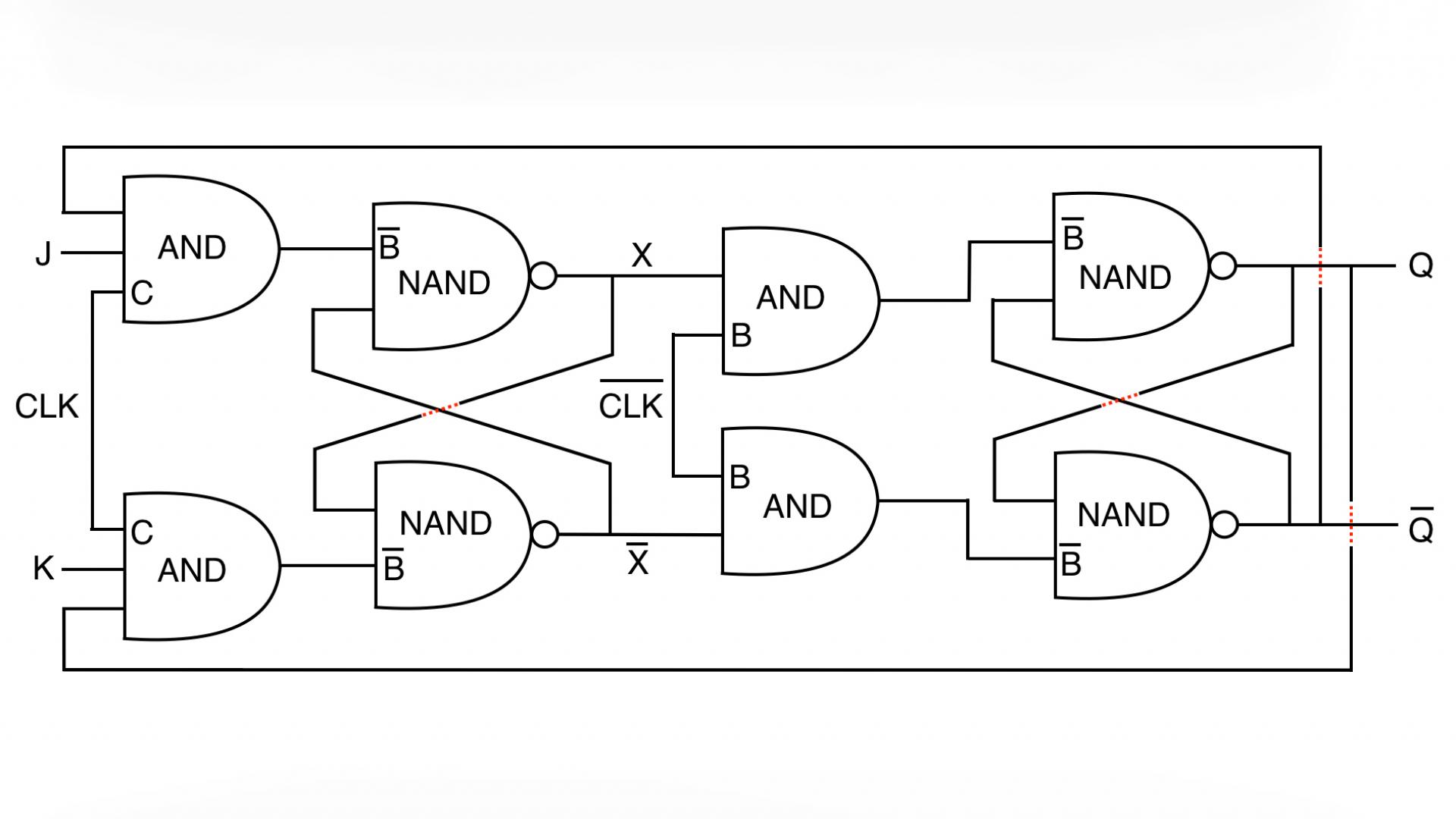
- Sequential circuits, including relay based latches and flip-flops
- Interface circuits, including relay based Analog-to-Digital (ADC) converter, and Digital-to-Analog (DAC) converter
- Energy management module, namely power gating CMOS circuit with relays
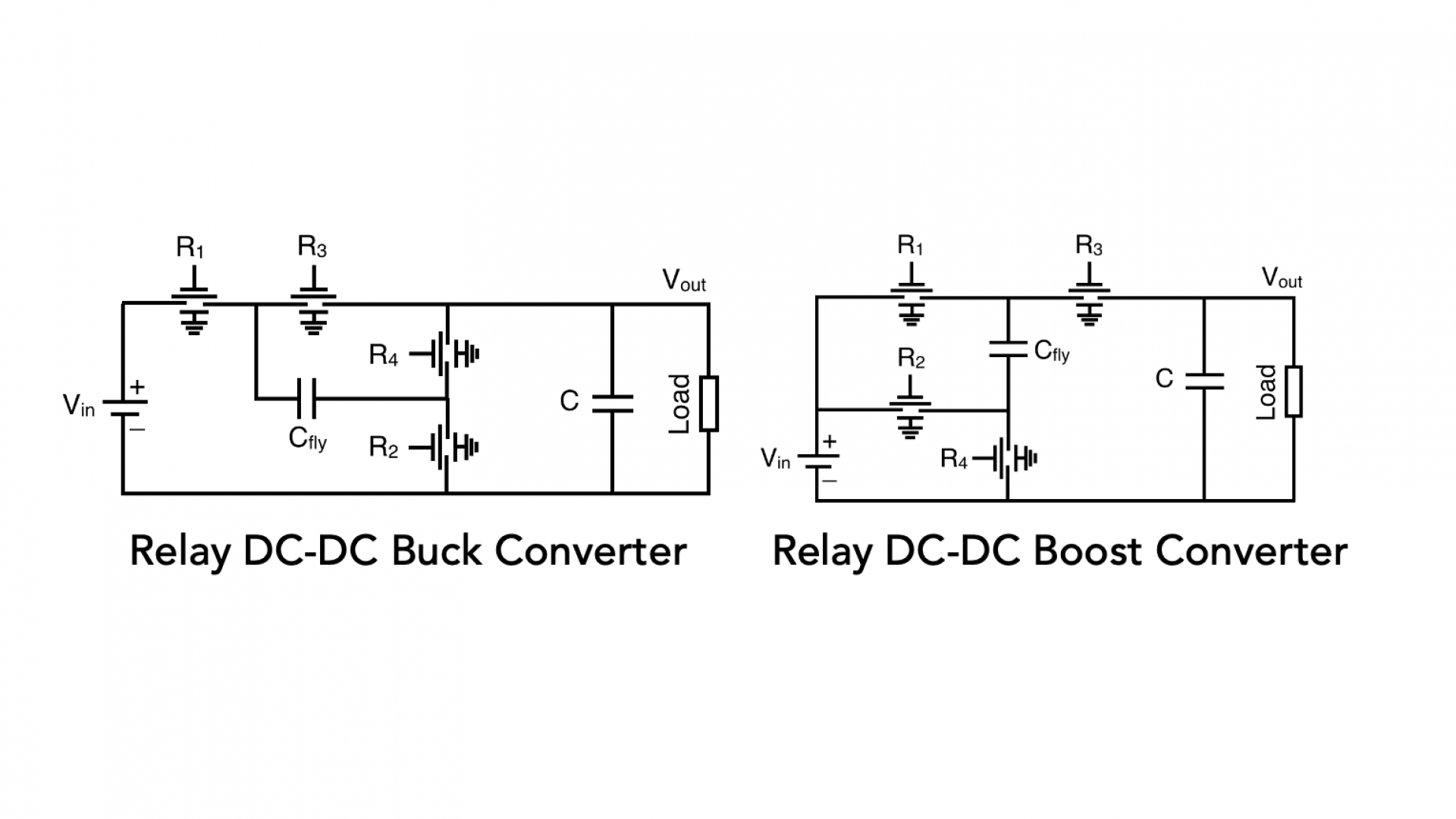
- On-Chip power converters, including relay based inductorless DC-DC buck converter and boost converter