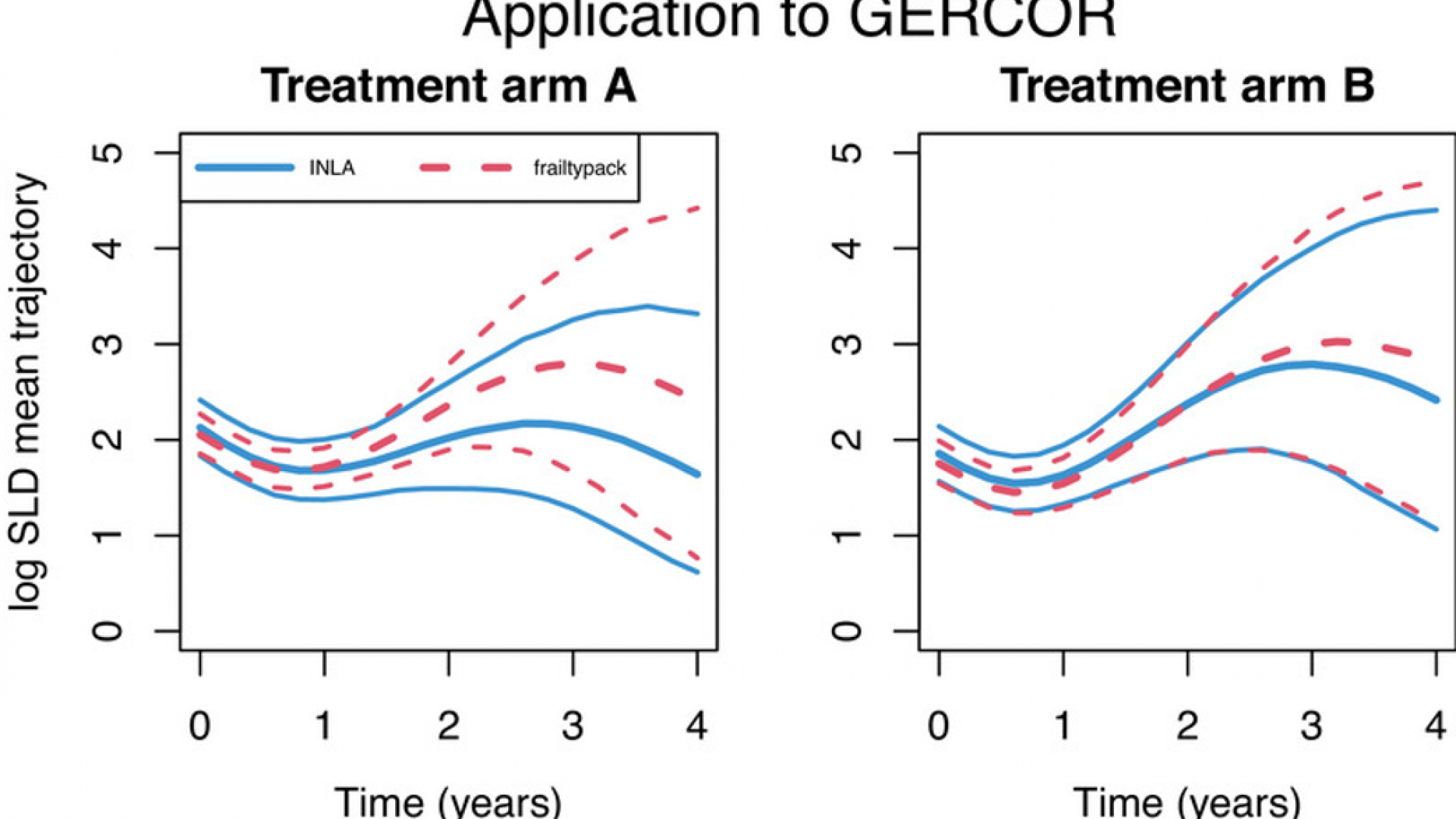
Two-part joint models for a longitudinal semicontinuous biomarker and a terminal event have been recently introduced based on frequentist estimation. The biomarker distribution is decomposed into a probability of positive value and the expected value among positive values. Shared random effects can represent the association structure between the biomarker and the terminal event.
A book chapter based on the use of INLA for efficient Bayesian modeling of interval-censored survival and reliability data has been published in the book Emerging Topics in Modeling Interval-Censored Survival Data<
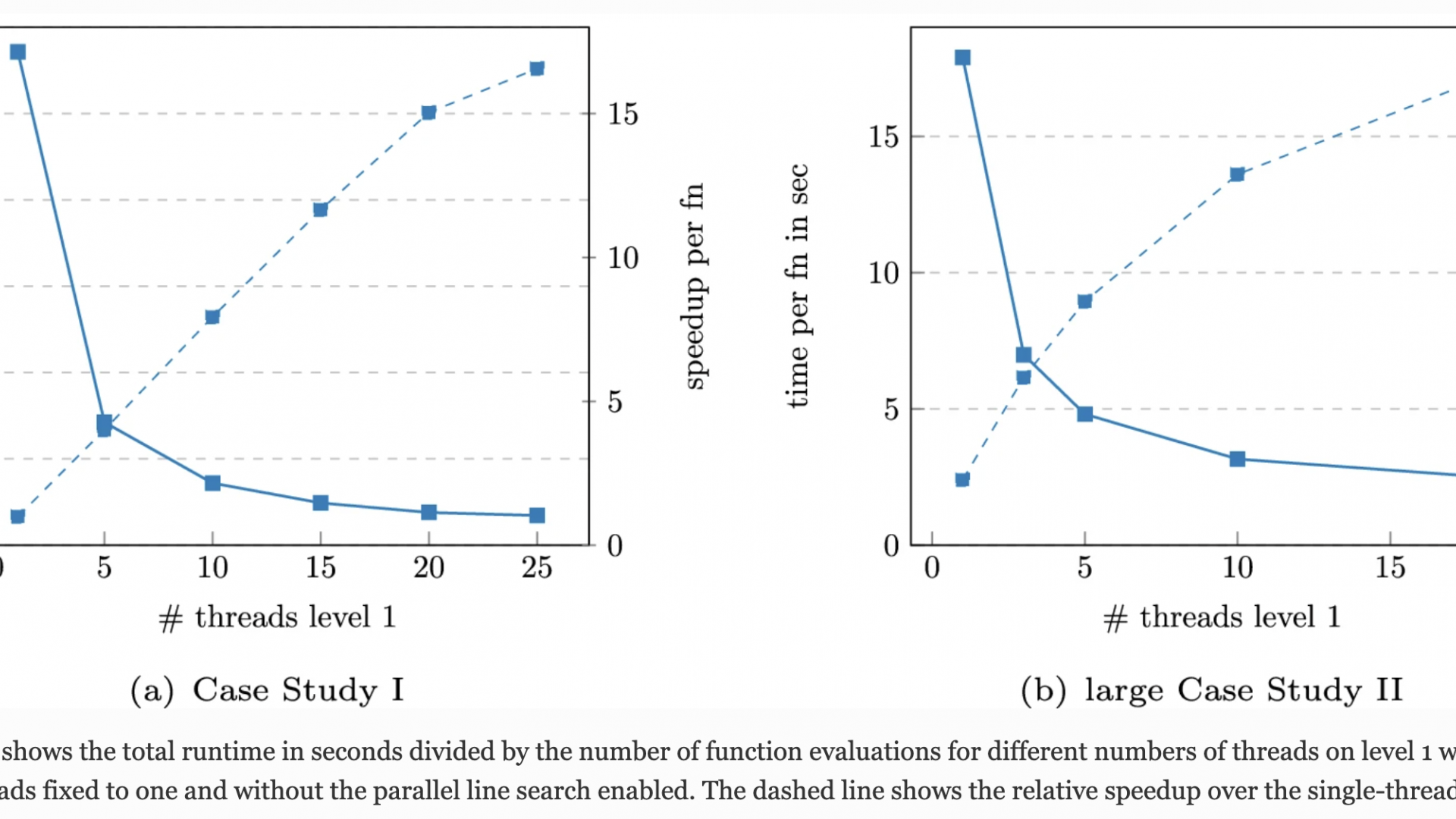
Members of the BayesComp group together with collaborators from UCI developed parallelization strategies for the methodology of integrated nested Laplace approximations (INLA). The approach makes use of nested thread-level parallelism, a parallel line search procedure using robust regression in INLA’s optimization phase and the state-of-the-art sparse linear solver PARDISO.
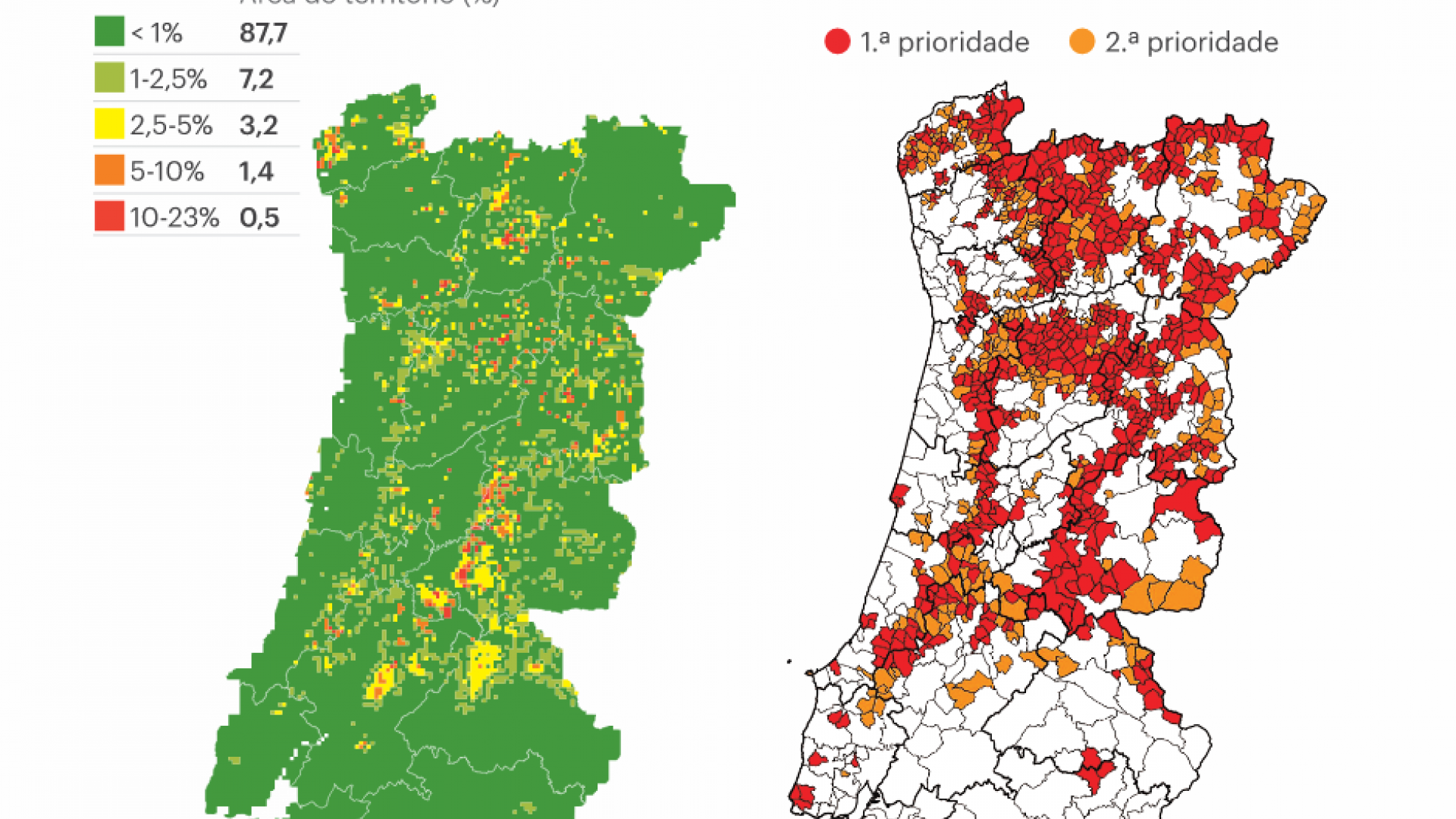
Professors Maria Antónia da Conceição Abrantes Amaral Turkman and
Kamil Feridum Turkman, from the University of Lisbon used the
INLA methodology and specifically SPDE's (using R-INLA), to do the official
risk assessment for forest fire prediction in Portugal for 2018.
New accepted paper: Lombardo, L., Bakka, H., Tanyas, H., van Westen, C., Mai, P.
New accepted paper: Castro-Camilo, D., Huser, R., and Rue, H.