Loïc Marnat, et al., "On-chip implantable antennas for wireless power and data transfer in a glaucoma monitoring SoC" IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters (11), 2012, 1671.
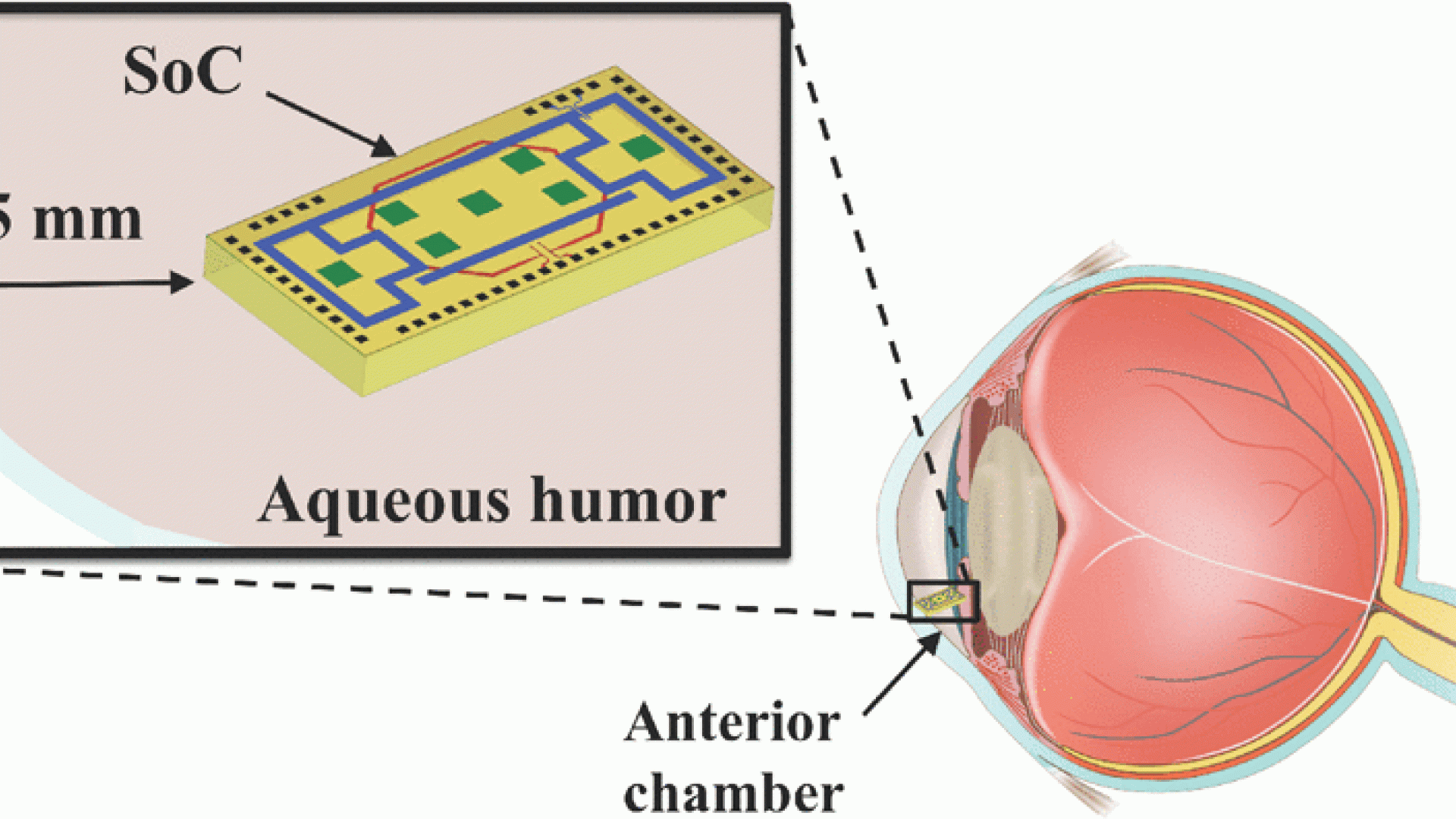
Abstract: For the first time, separate transmit and receive on-chip antennas have been designed in an eye environment for implantable intraocular pressure monitoring application. The miniaturized antennas fit on a 1.4-mm 3 CMOS (0.18 μm) chip with the rest of the circuitry. A 5.2-GHz novel inductive-fed and loaded receive monopole antenna is used for wirelessly powering the chip and is conjugately matched to the rectifier in the energy-harvesting and storage unit. The 2.4-GHz transmit antenna is an octagonal loop that also acts as the inductor of the voltage control oscillator resonant tank. To emulate the eye environment in measurements, a custom test setup is developed that comprises Plexiglass cavities filled with saline solution. A transition, employing a balun, is also designed, which transforms the differential impedance of on-chip antennas immersed in saline solution to a 50-Ω single-ended microstrip line. The antennas on a lossy Si substrate and eye environment provide sufficient gain to establish wireless communication with an external reader placed a few centimeters away from the eye.