Ultrathin needles for probing plants could help keep crop health in check.
A neural network that mimics the biology of the brain can be loaded onto a microchip for faster and more efficient artificial intelligence.
An assistive technology uses magnetic skin to support freedom of movement for people with quadriplegia.
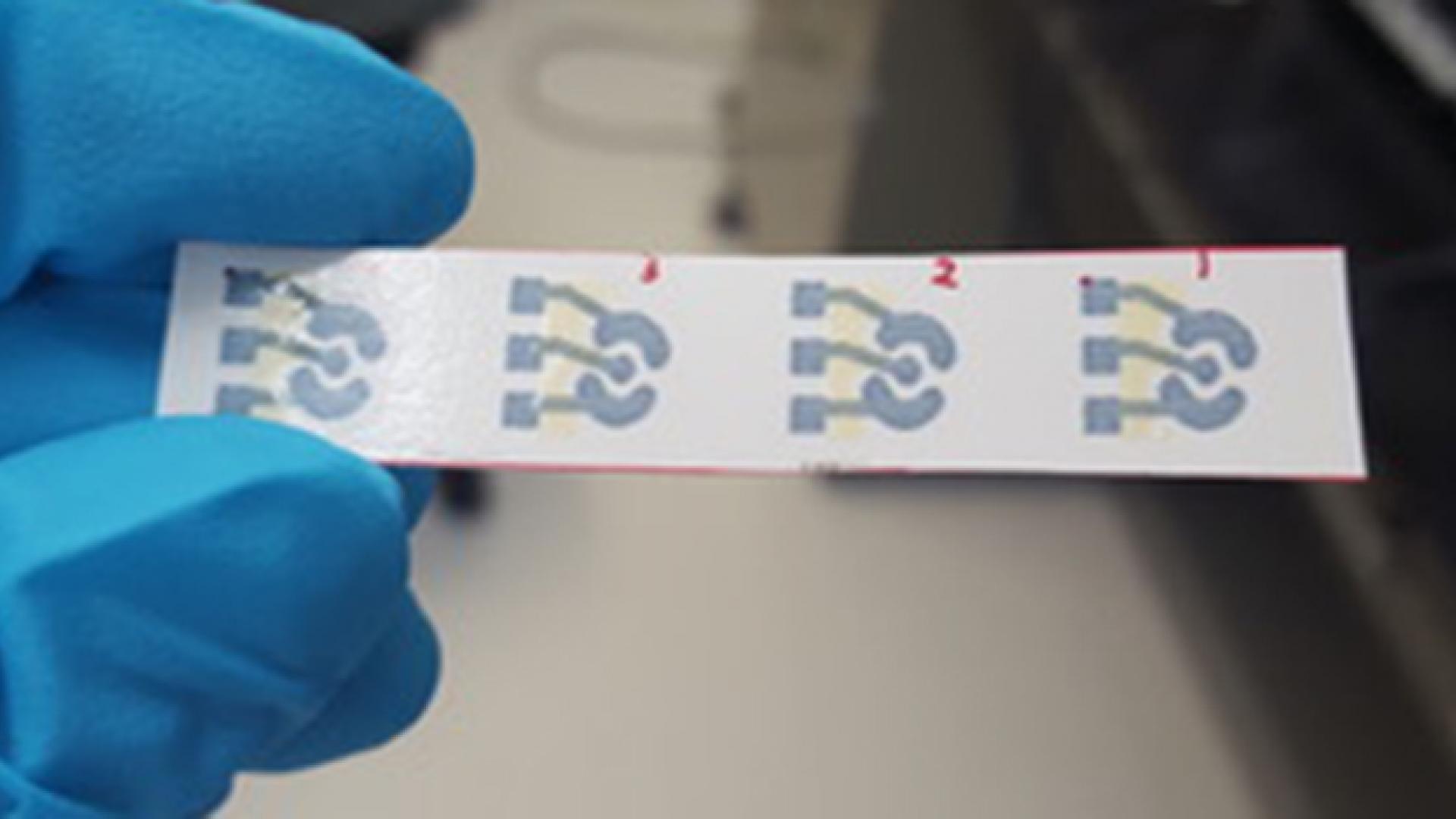
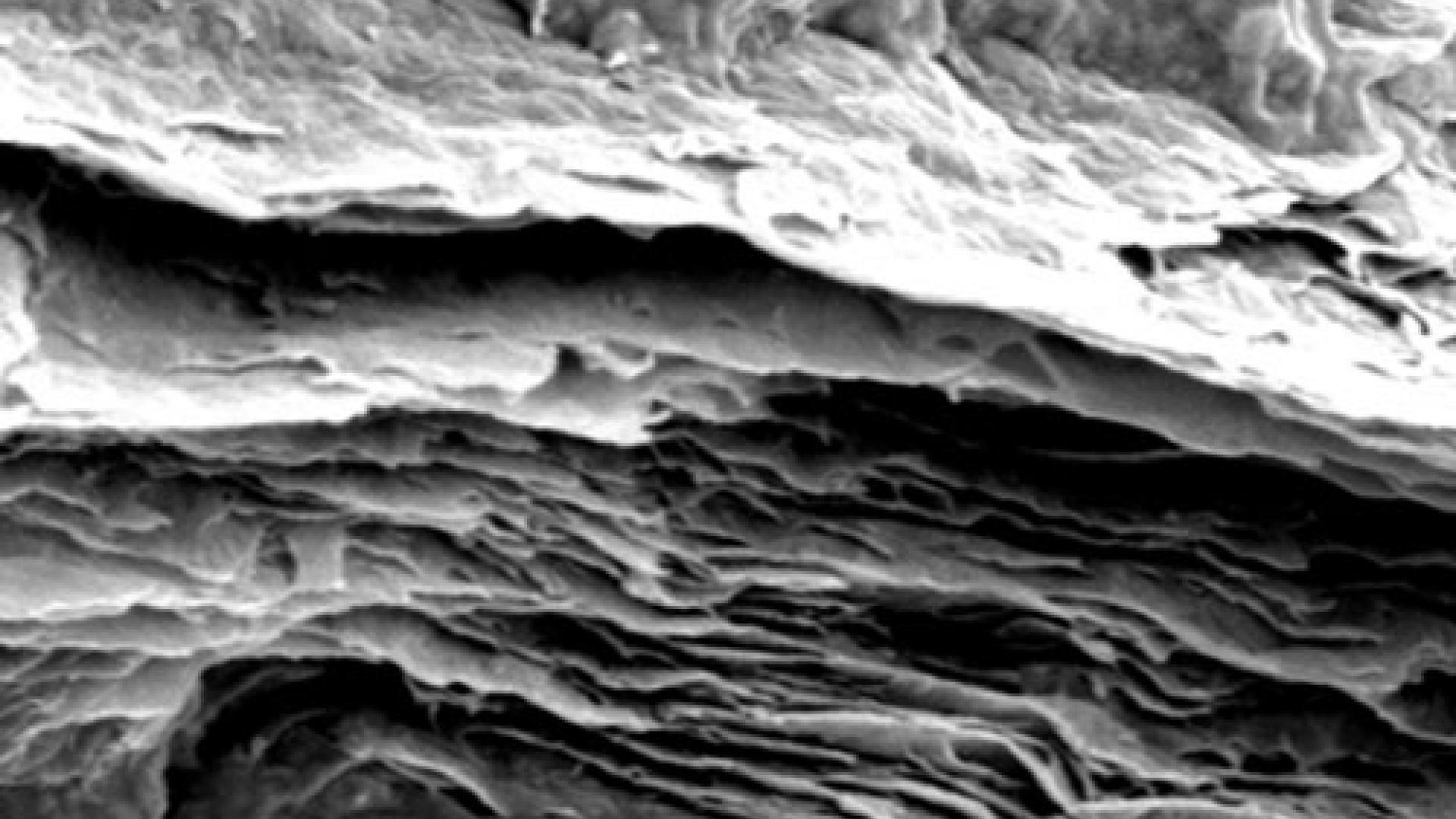
Laser writing breathes life into high-performance sensing platforms.
In today’s world, it should come as no surprise that plastic dominates the products that we rely on each and every day. From our technology devices, to our water bottles, plastic is almost always an integral structural component.
An integrated detector device could form the basis of a distributed air-quality sensor network.
Nanomaterial-based electronic device monitors a key heart health biomarker.
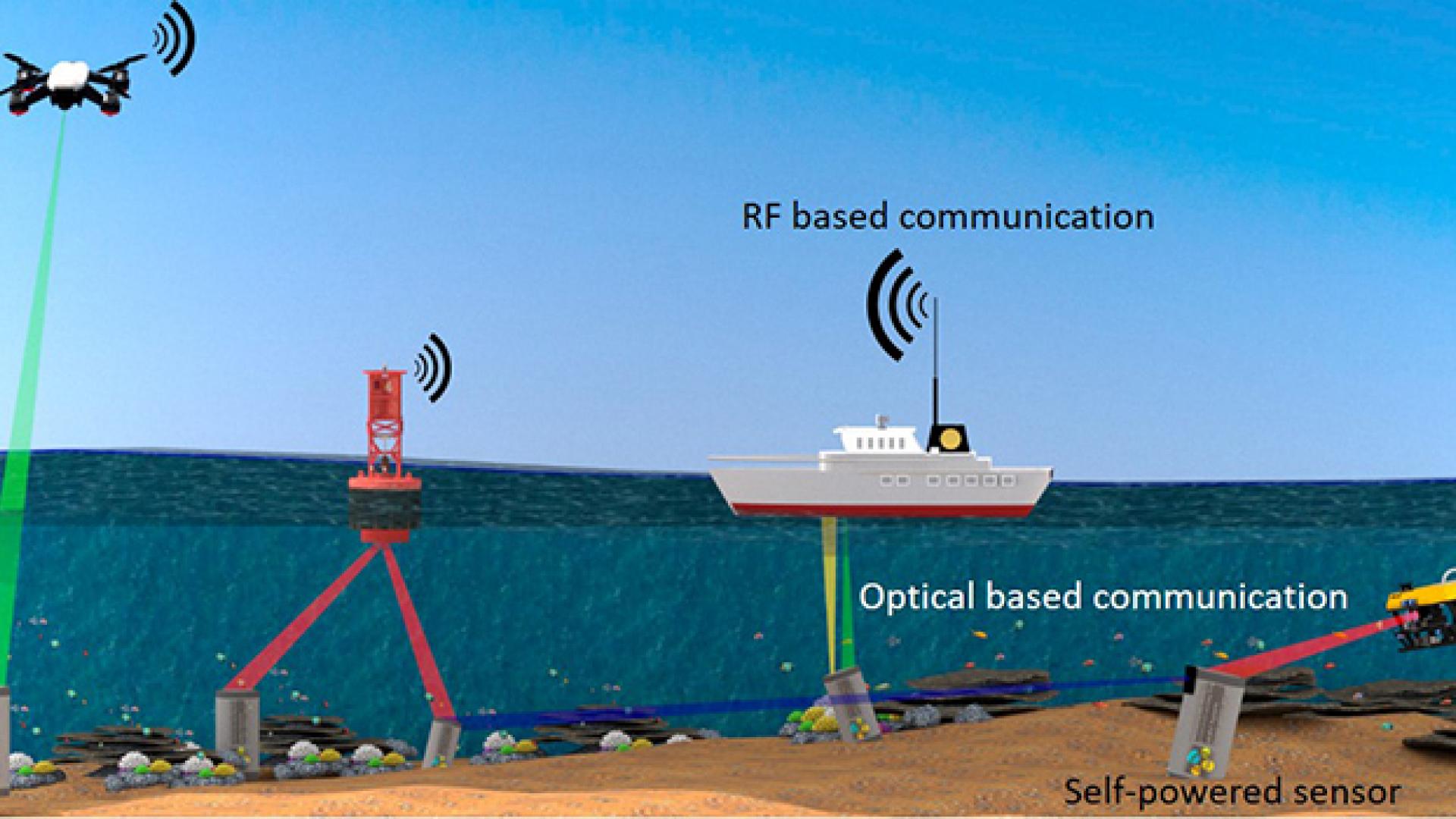
Light can simultaneously transfer energy and data to underwater devices, but there’s a long way to go before these systems can be deployed.
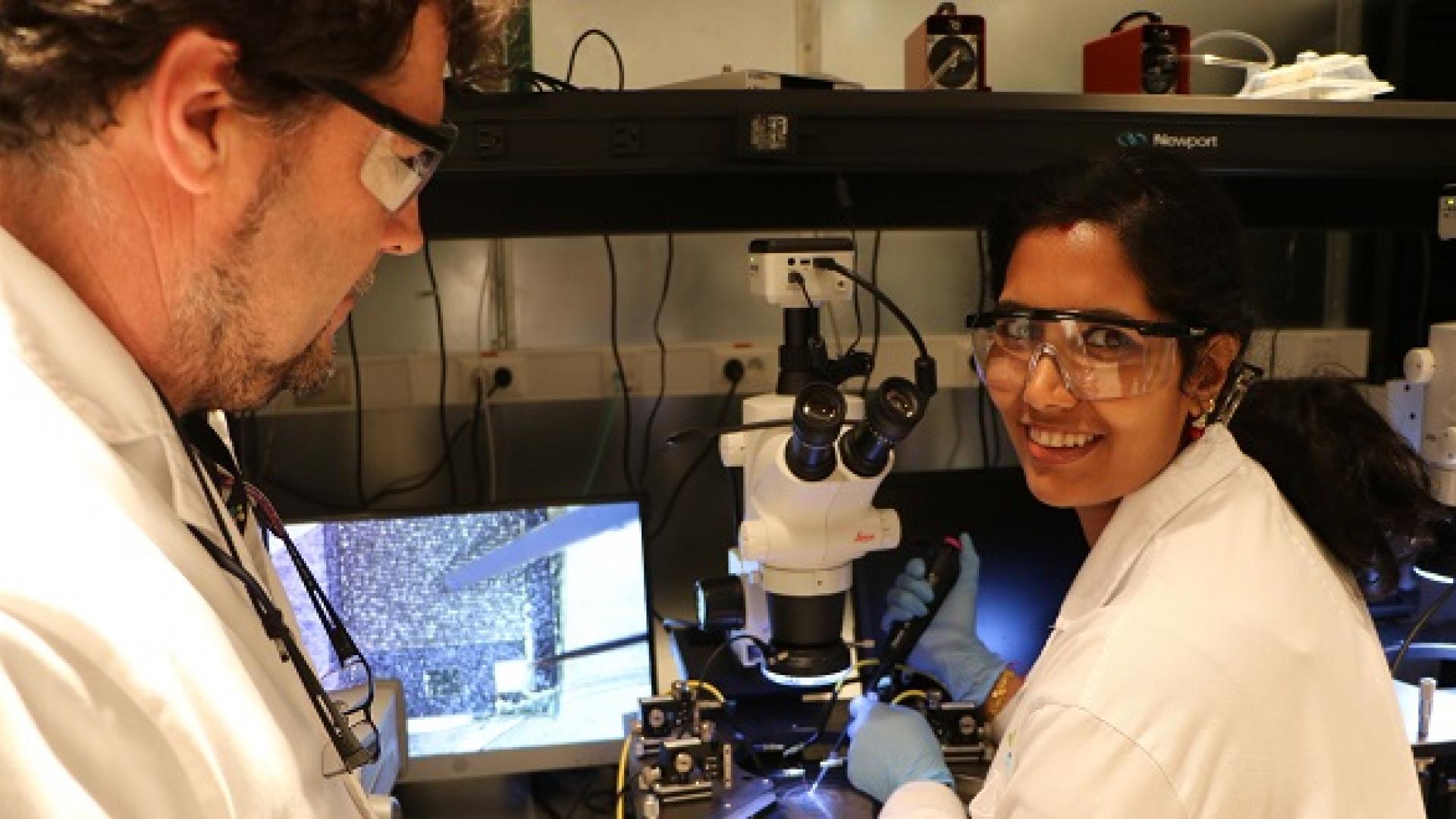
What do an electrical engineer, an organic chemist, a materials scientist and a cell biologist all have in common? They invent and improve applications at the interface of biology and electronics.
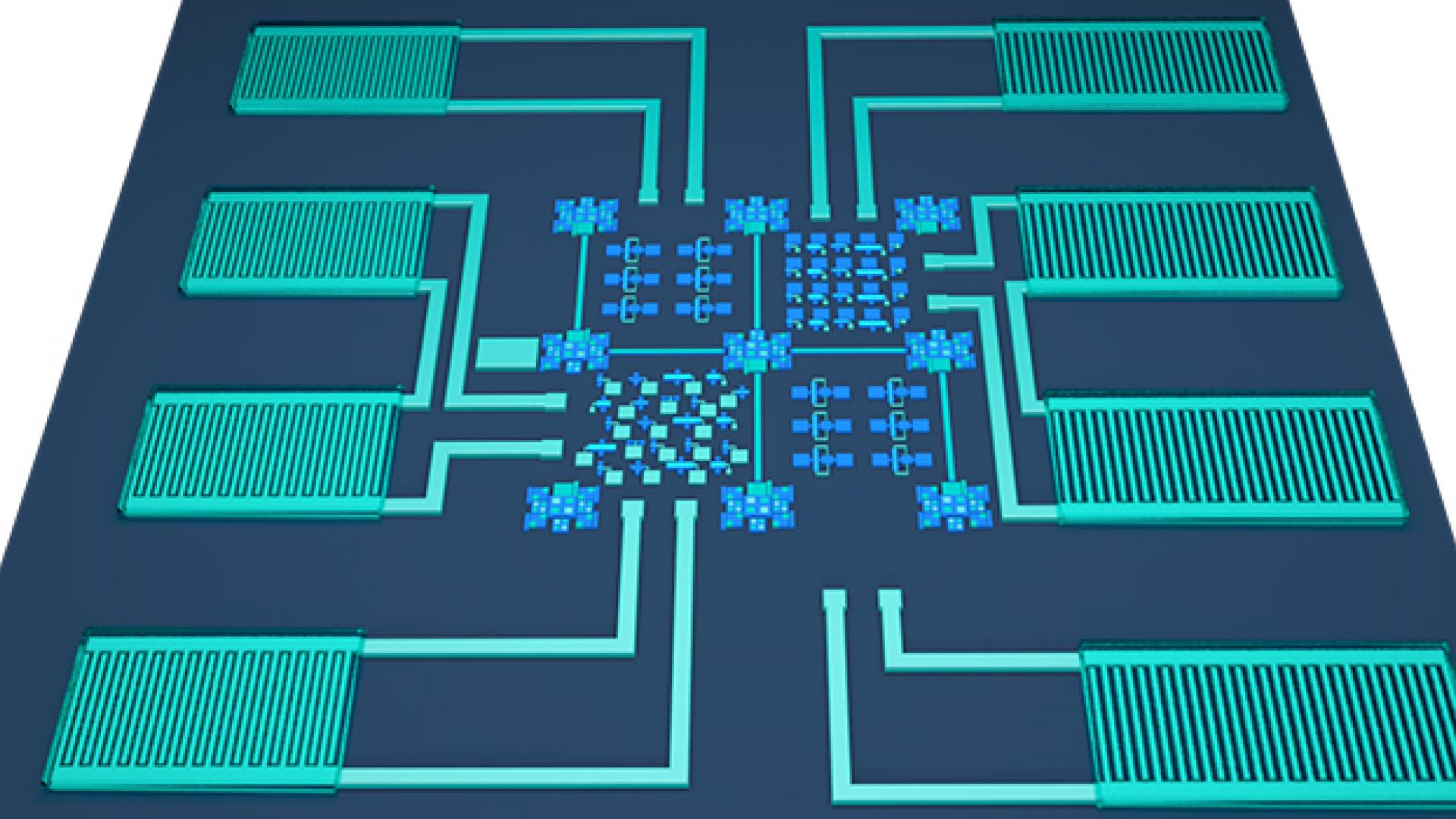
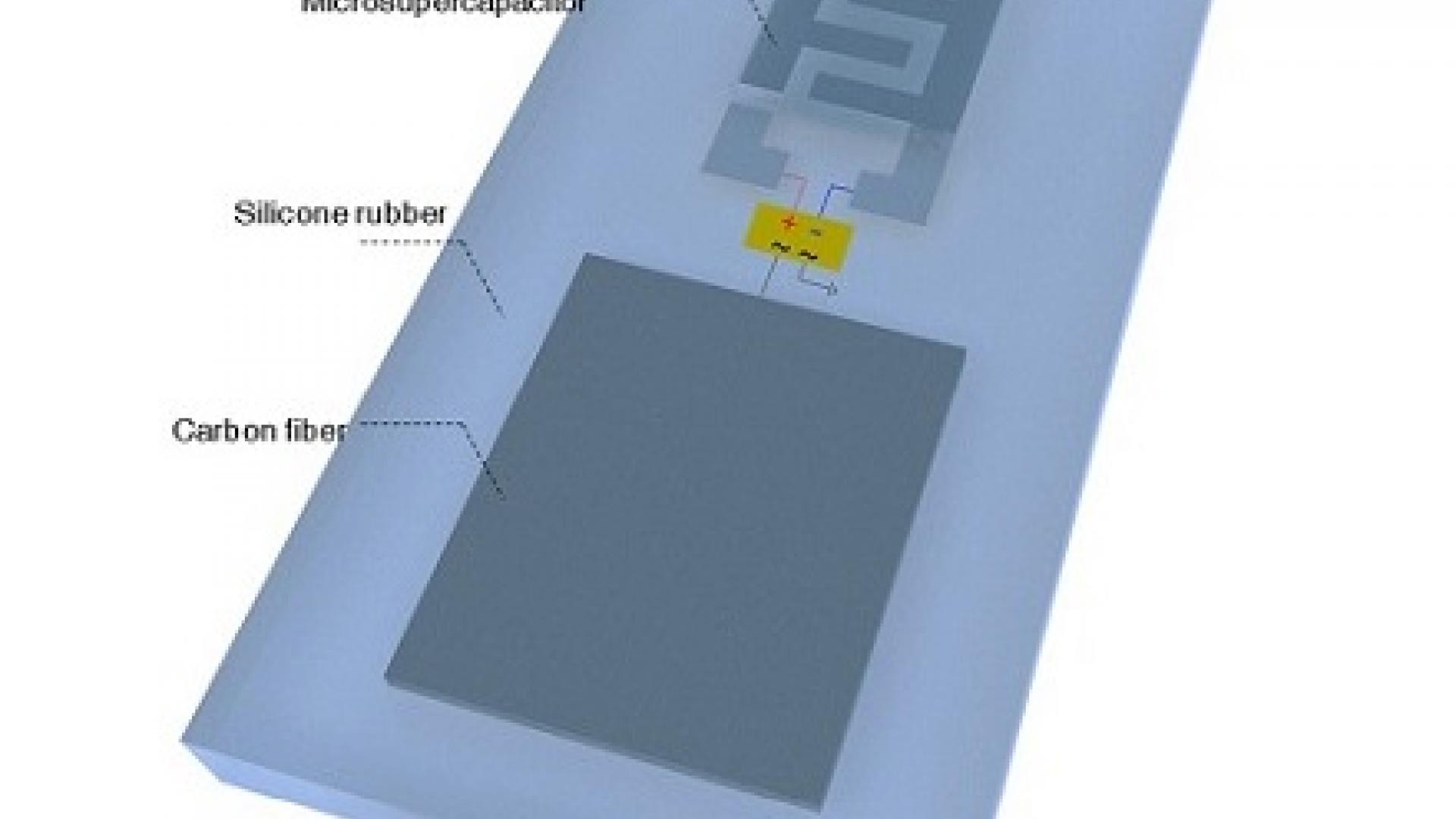
Ruthenium oxide is used to integrate energy-storing microsupercapacitors and thin-film electronics at the transistor level.
An interdisciplinary initiative is helping KAUST be at the forefront of a digital revolution, where sensors can find a use just about anywhere.
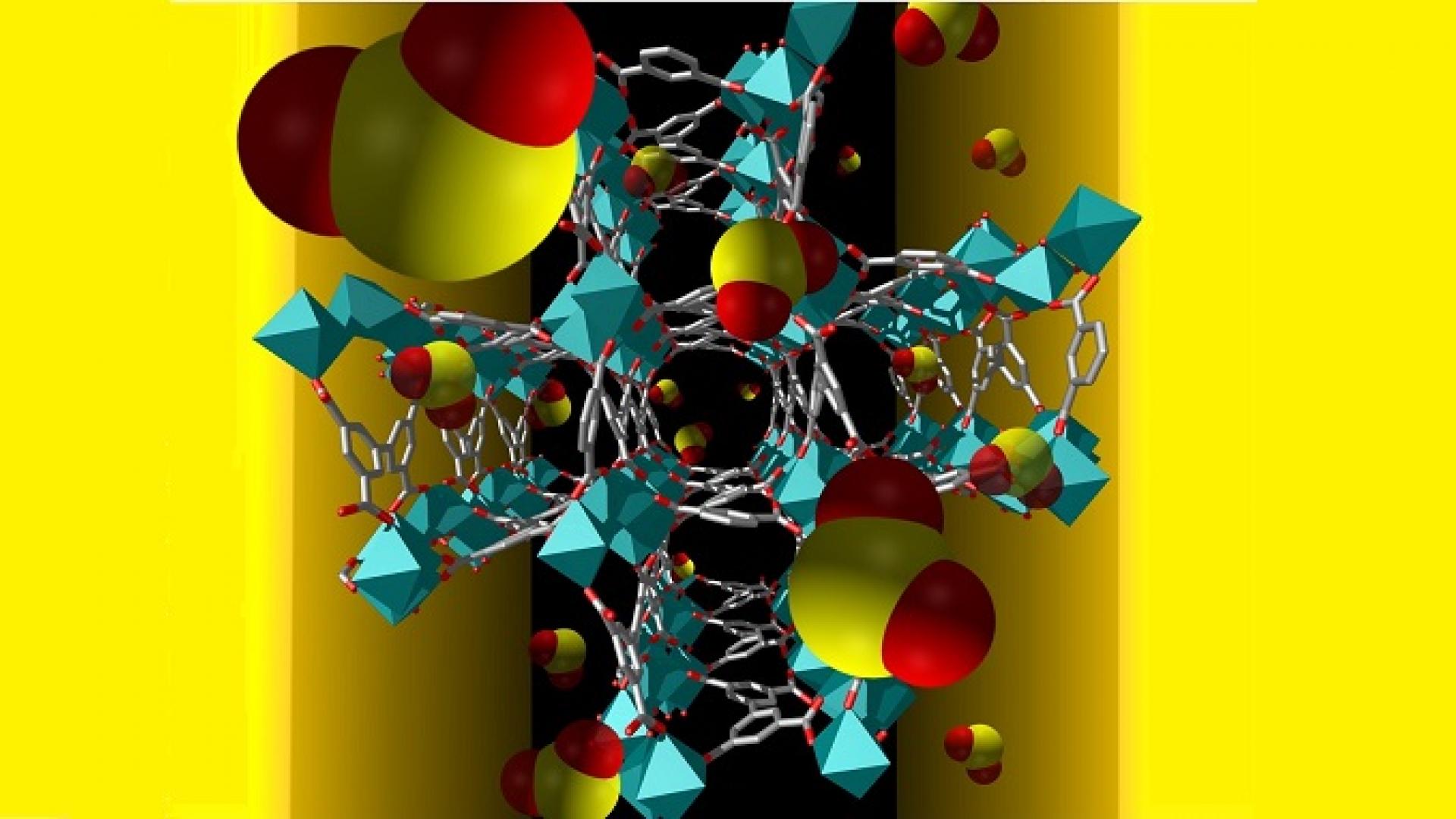
Fluorinated metal-organic frameworks make excellent materials for selective sensing and removal of toxic gases.
A simple fractional-order capacitor has been developed by a team from KAUST. Made from a single component, this device expands the range of frequencies that can be achieved by these devices, making them better at energy storage. Traditional analogue components are resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
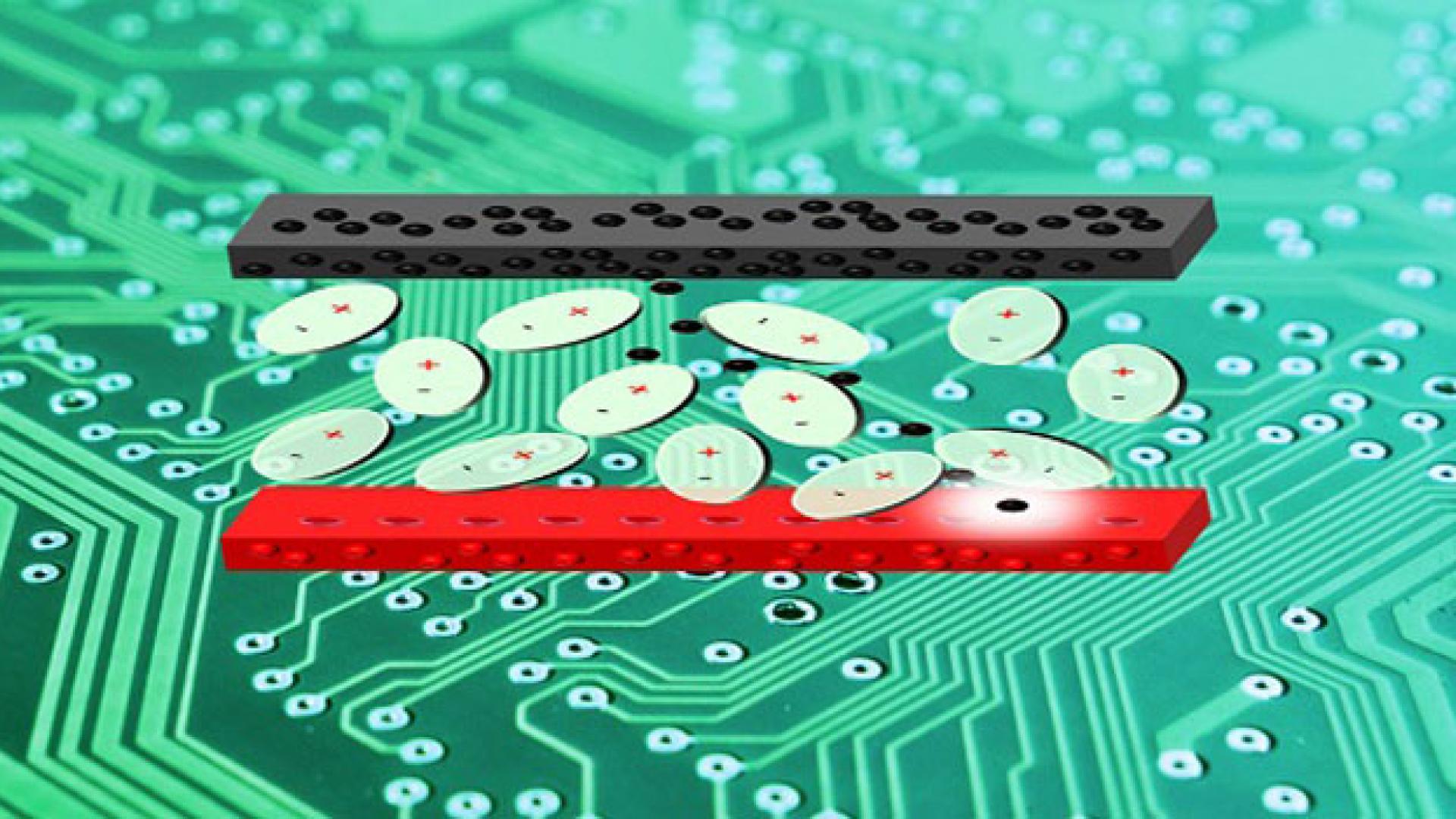
Ambient energy emitted by cellular phones and modems can be captured and converted into electricity using unusually shaped technology.
Inkjet-printed device helps monitor a patient’s blood sugar levels without painful needles.
A porous material with tailor-made pockets stitched into its structure is a promising material for sensing noxious gases. A thin film of the material, coated onto an electrode, formed an electronic sensor that could detect traces of sulfur dioxide gas.
Standalone power modules that harvest and convert vibrations from their surroundings into electricity could soon fuel future microsystems.
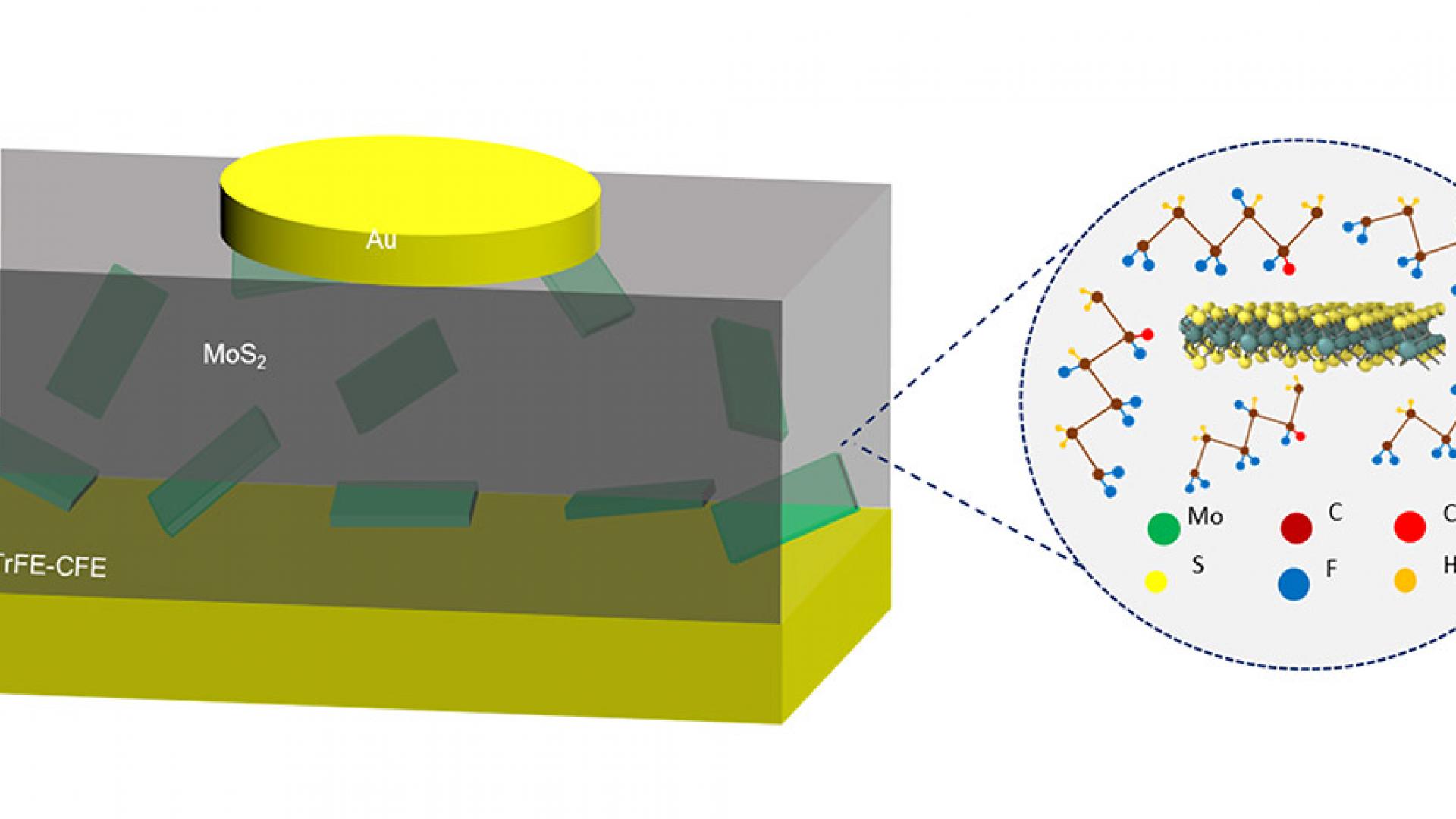
A novel type of electronic component made from a blend of polymer materials could enable more effective circuitry.
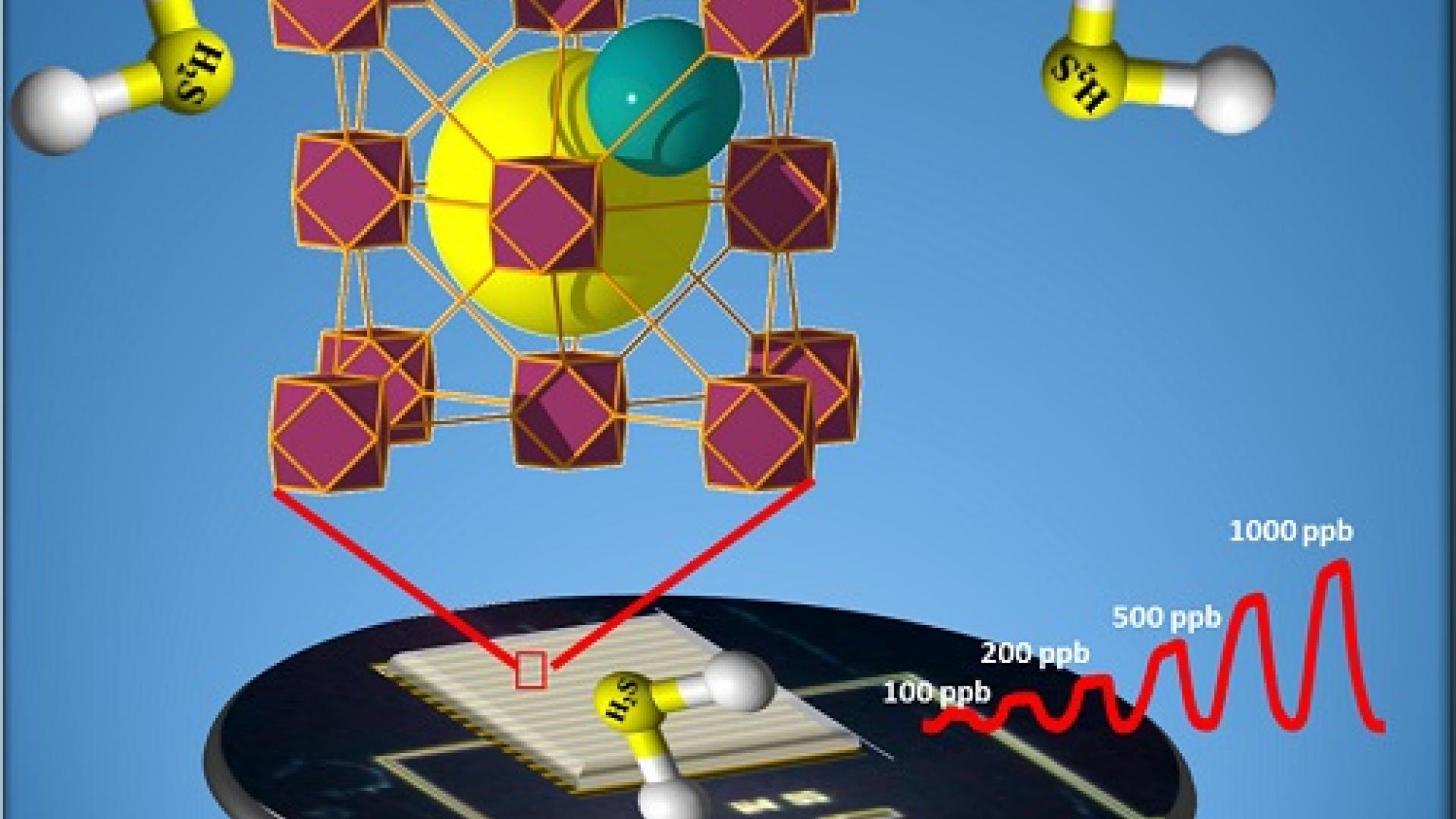
Tunable porous MOF materials interface with electrodes to sound the alarm at the first sniff of hydrogen sulfide.
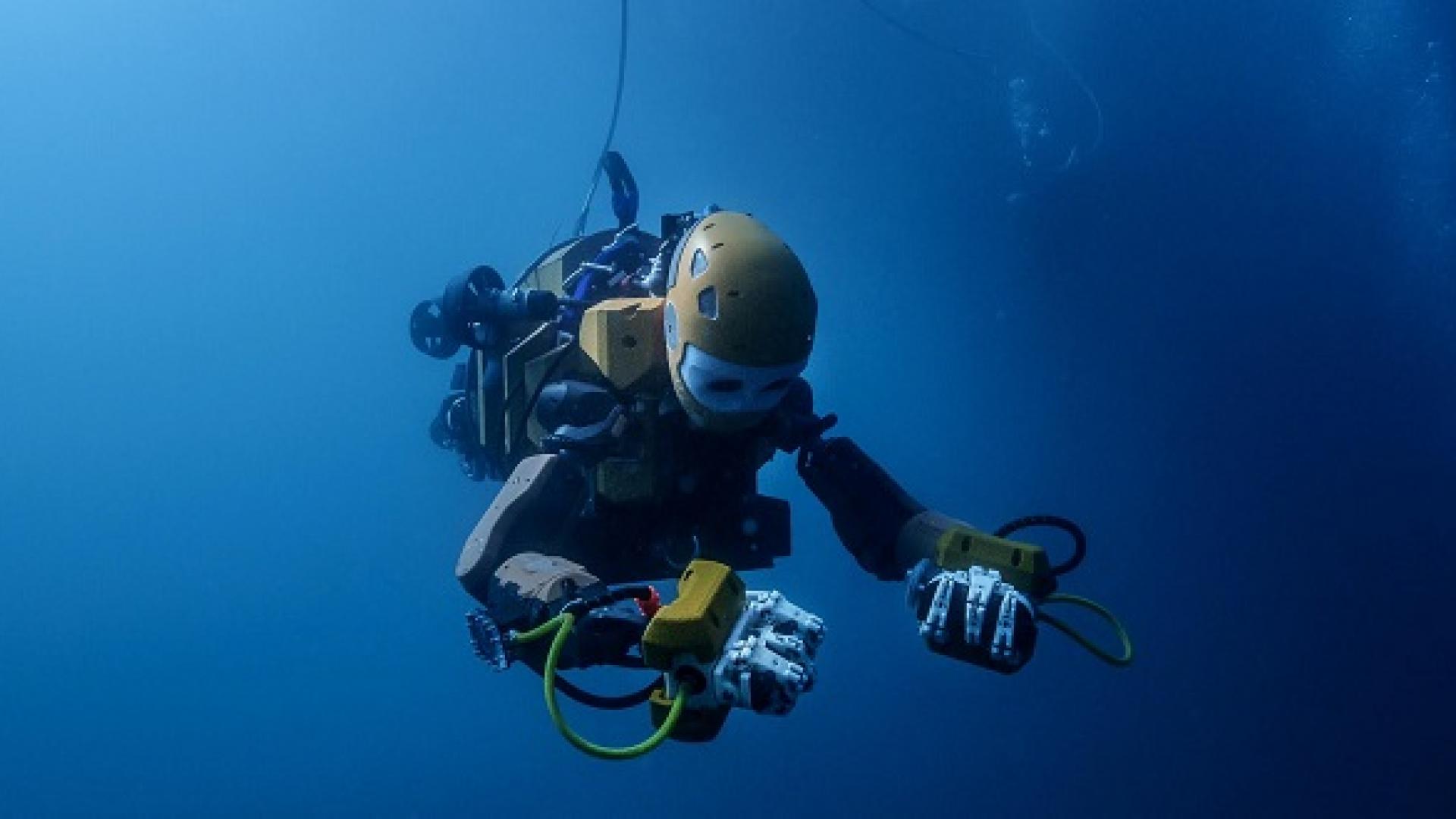
An international, multidisciplinary collaboration that led to the world’s first underwater robotic avatar.
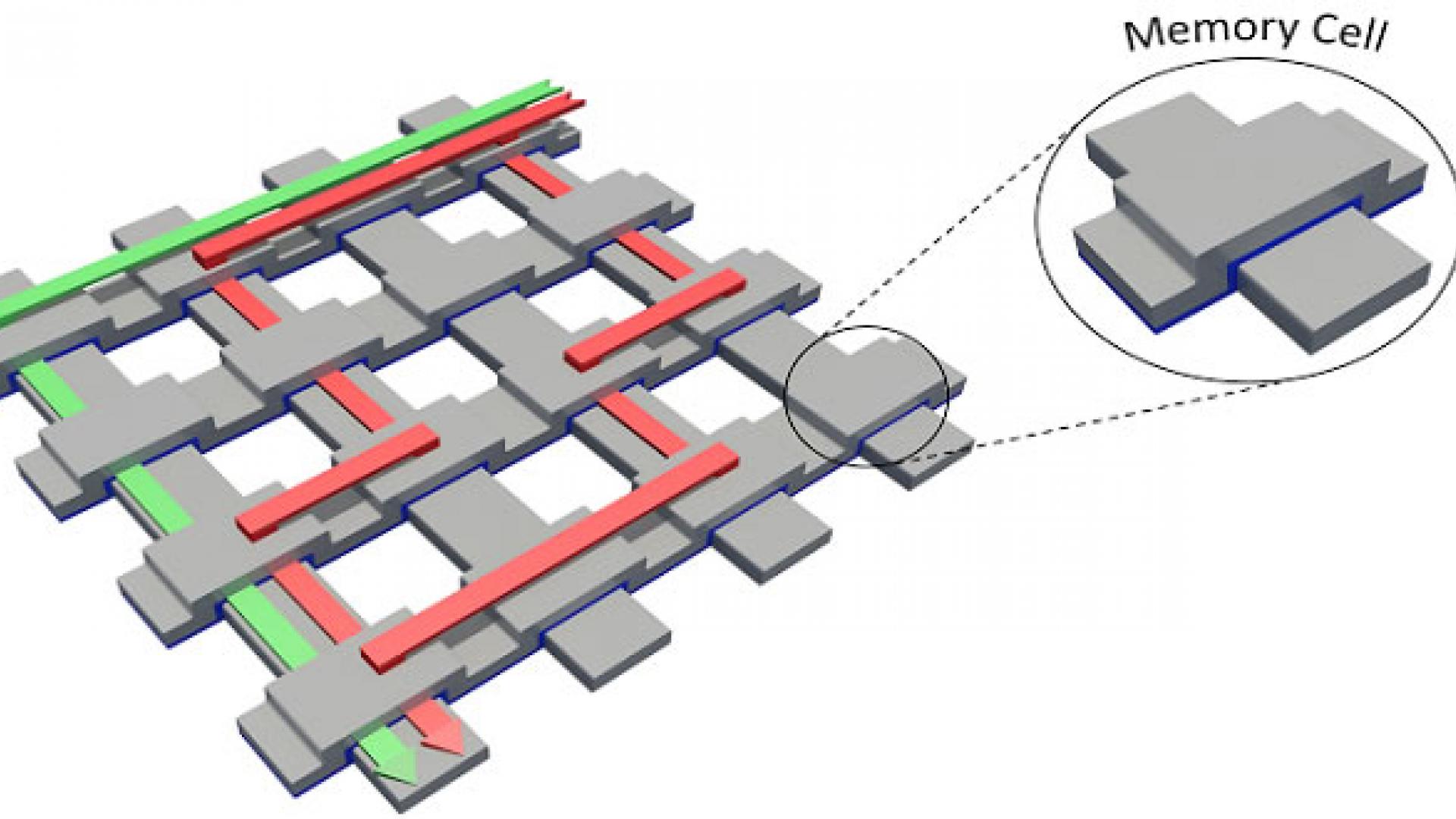
A data readout scheme achieves an unprecedented reduction in power consumption for a promising high-performance resistive memory architecture.
A new biosensor made of laser-etched electrodes on a gold-coated polymer may provide an effective and cost-efficient way to assess heart disease risk.
A tiny device broadens the bandwith to enable absorption with wide-reaching potential for electrical engineering.
Graphene-based capacitors prove useful in advanced non-linear electronics.