Yousof Mashraei, et al., "Integration of fractal biosensor in a digital microfluidic platform." IEEE Sensors Journal 16 (24), 2016, 8775.
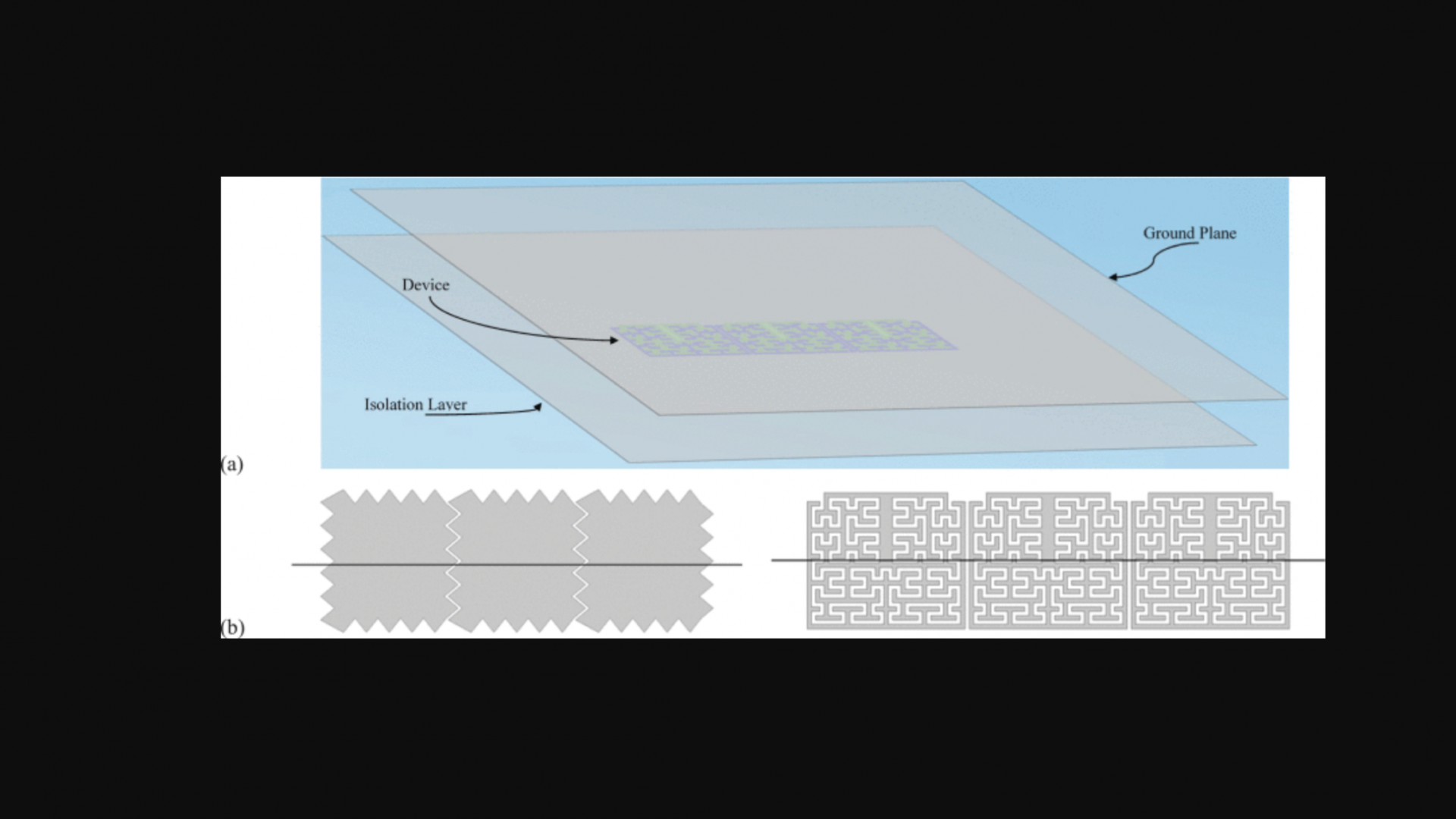
Abstract: The digital microfluidic (DMF) platform introduces many applications in biomedical assays. If it is to be commercially available to the public, it needs to have the essential features of smart sensing and a compact size. In this paper, we report on a fractal electrode biosensor that is used for both droplet actuation and sensing C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration levels to assess cardiac disease risk. Our proposed electrode is the first two-terminal electrode design to be integrated into DMF platforms. A simulation of the electrical field distribution shows reduced peak intensities and uniform distribution of the field. When compared with a V-notch square electrode, the fractal electrode shows a superior performance in both aspects, i.e., field uniformity and intensity. These improvements are translated into a successful and responsive actuation of a water droplet with 100 V. Likewise, the effective dielectric strength is improved by a 33% increase in the fractal electrode breakdown voltage. In addition, the capability of the fractal electrode to work as a capacitive biosensor is evaluated with CRP quantification test. Selected fractal electrodes undergo a surface treatment to immobilize anti-CRP antibodies on their surface. The measurement shows a response to the added CRP in capacitance within 3 min. When the untreated electrodes were used for quantification, there was no significant change in capacitance, and this suggested that immobilization was necessary. The electrodes configuration in the fabricated DMF platform allows the fractal electrodes to be selectively used as biosensors, which means that the device could be integrated into point-of-care applications.