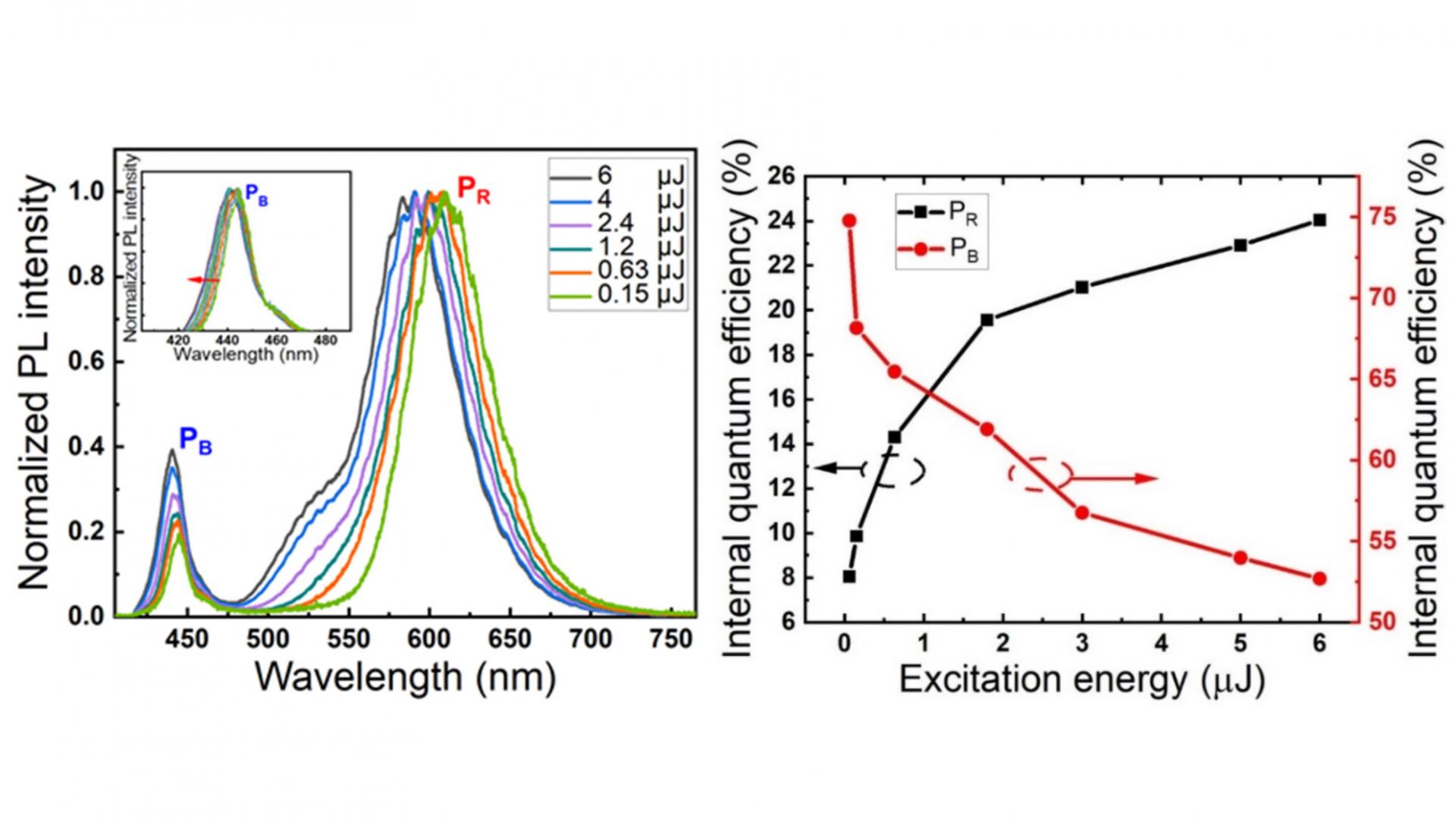
[Abstract] Optical properties of InGaN-based red LED structure, with a blue pre-well, are reported. Two emission peaks located at 445.1 nm (PB) and 617.9 nm (PR) are observed in the PL spectrum, which are induced by a low-In-content blue InGaN single quantum well (SQW) and the red InGaN double quantum wells (DQWs), respectively. The peak shift of PB with increase of excitation energy is very small, which reflects the built-in electric field of PB-related InGaN single QW is remarkably decreased, being attributed to the significant reduction of residual stress in the LED structure. On the other hand, the PR peak showed a larger shift with increase of excitation energy, due to both the screening of built-in electric field and the band filling effect. The electric field in the red wells is caused by the large lattice mismatch between high-In-content red-emitting InGaN and surrounding GaN. In addition, the anomalous temperature dependences of the PR peak are well elucidated by assuming that the red emission comes from quasi-QD structures with deep localized states. The deep localization suppresses efficiently the escape of carriers and then enhances the emission in the red, leading to high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of 24.03%.