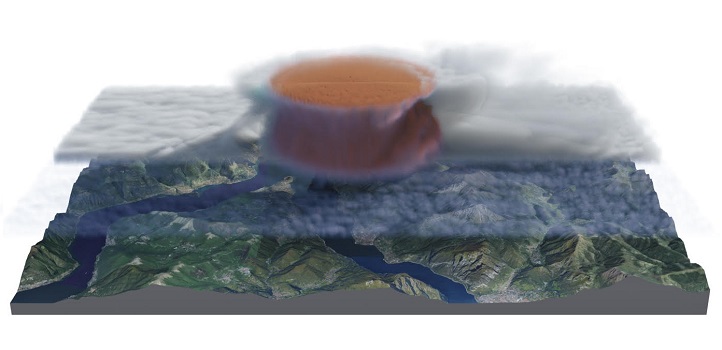
A cloud simulation that captures the development and evolution of clouds based on atmospheric physical processes is more accurate than other models.
“Our model describes atmospheric conditions and thermodynamic processes as well as the fluid dynamics that govern the motion of air in the atmosphere,” says Torsten Hädrich, a KAUST Ph.D. student in the international research team. “This allows us to simulate cloud phenomena more realistically than previous methods.”
The model can take known atmospheric information at any time, such as temperature, humidity and wind, and simulate cloud formation, which is used for "nowcasting" of imminent cloud phenomena.
“For example, our model is able to simulate the formation of cumulonimbus clouds by considering varying temperature gradients in the atmosphere,” says Hädrich. “The gradients lead to temperature inversions at certain altitudes, which are responsible for the characteristic flattened top of cumulonimbus clouds. We can also model different types of supercell thunderstorms, which has not been addressed previously.”
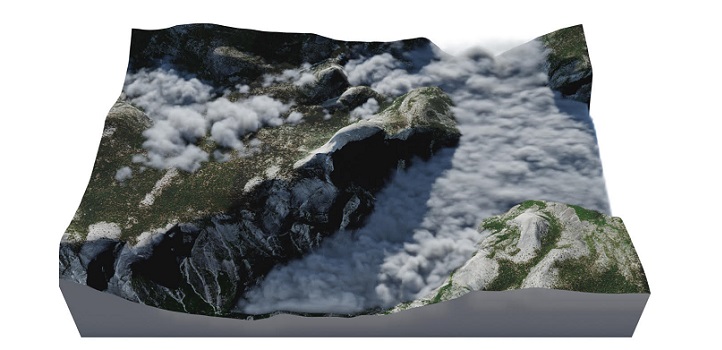
The model was developed by KAUST's Hädrich and Dominik Michels in collaboration with researchers from Adam Mickiewicz University in Poland, the University of New Mexico in the U.S. and Google AI.
Read the full article

