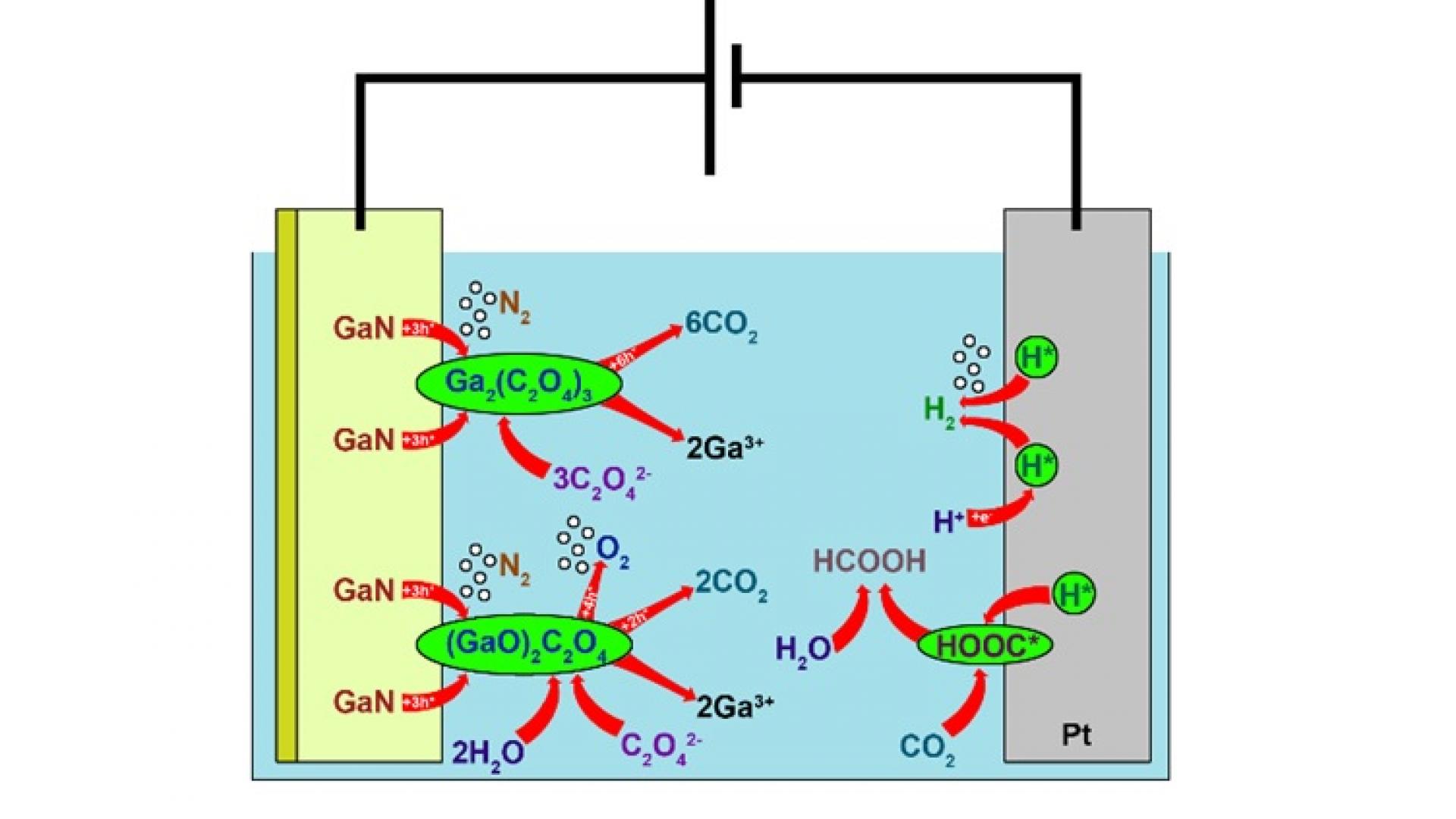
The paper reports the investigation of the wet electrochemical etching of n-GaN films in oxalic acid. The results of a number of quantitative physicochemical analysis methods of the products indicated a 6-electron nature of the etching reaction and fully revealed the mechanism of EC oxidation of n-GaN, which includes the formation of intermediates formed by adsorption of the solvent on GaN surface. Clear understanding of this reaction creates a solid foundation for the investigation of transformations of more complicated III-nitride systems for low-damage and high-precision processing of nitride-based devices.
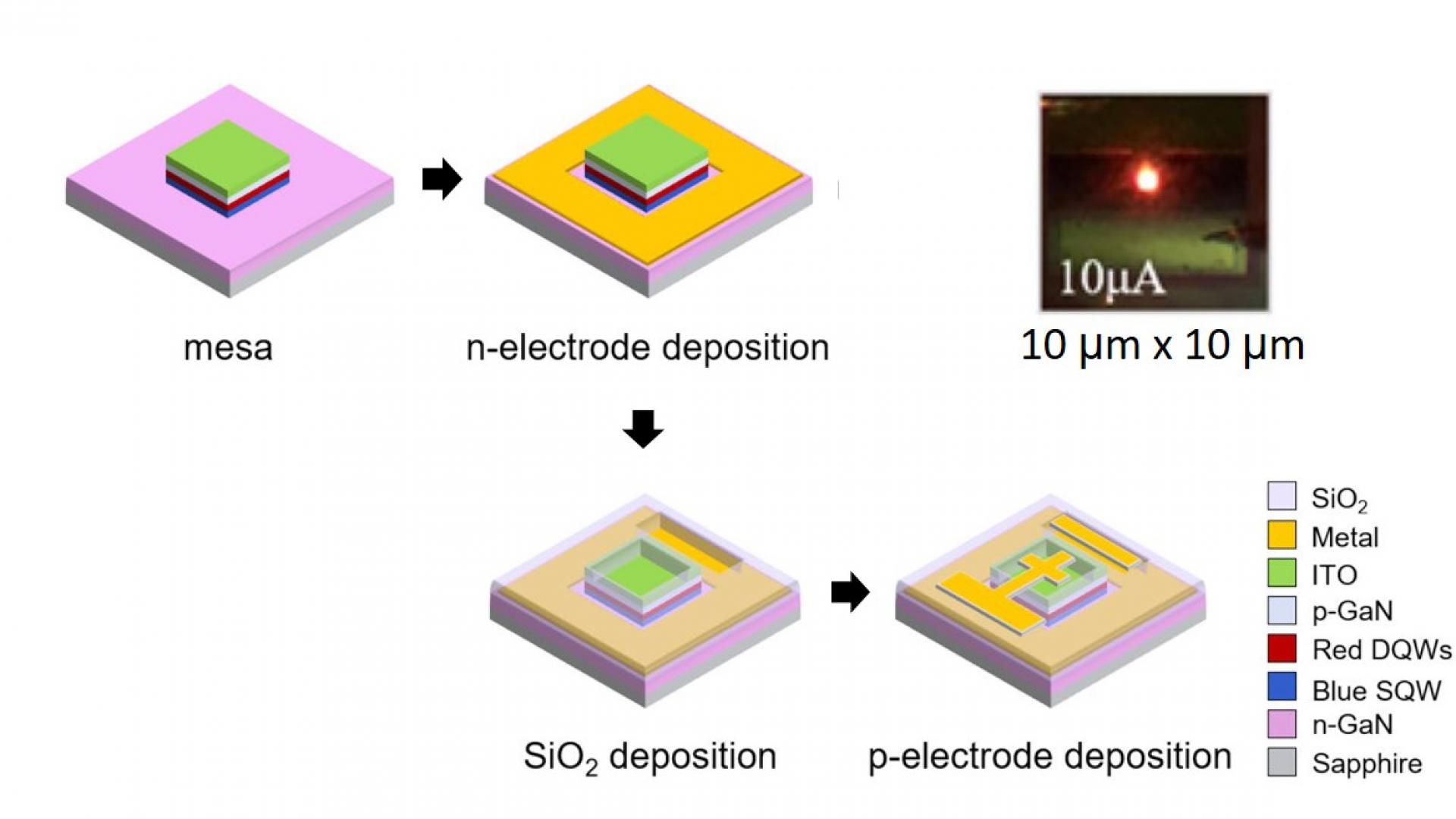
In this research, five sizes (100 × 100, 75 × 75, 50 × 50, 25 × 25, 10 × 10 μm2) of InGaN red micro-light emitting diode (LED) dies are produced using laser-based direct writing and maskless technology. It is observed that with increasing injection current, the smaller the size of the micro-LED, the more obvious the blue shift of the emission wavelength. When the injection current is increased from 0.1 to 1 mA, the emission wavelength of the 10 × 10 μm2 micro-LED is shifted from 617.15 to 576.87 nm.
The obvious blue shift is attributed to the stress release and high current density injection.
ECO Devices Lab welcomes Bei Ma as a Visiting Faculty. She is an Assistant Professor at Chiba University in Japan.
This talk will provide an overview of the III-nitride-based visible light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Especially, the InGaN-based blue LEDs are very contributed to energy-saving for light sources all over the world.
Tiny light-emitting devices that can create all the colors in the rainbow are essential for the next generation of phones and screens.
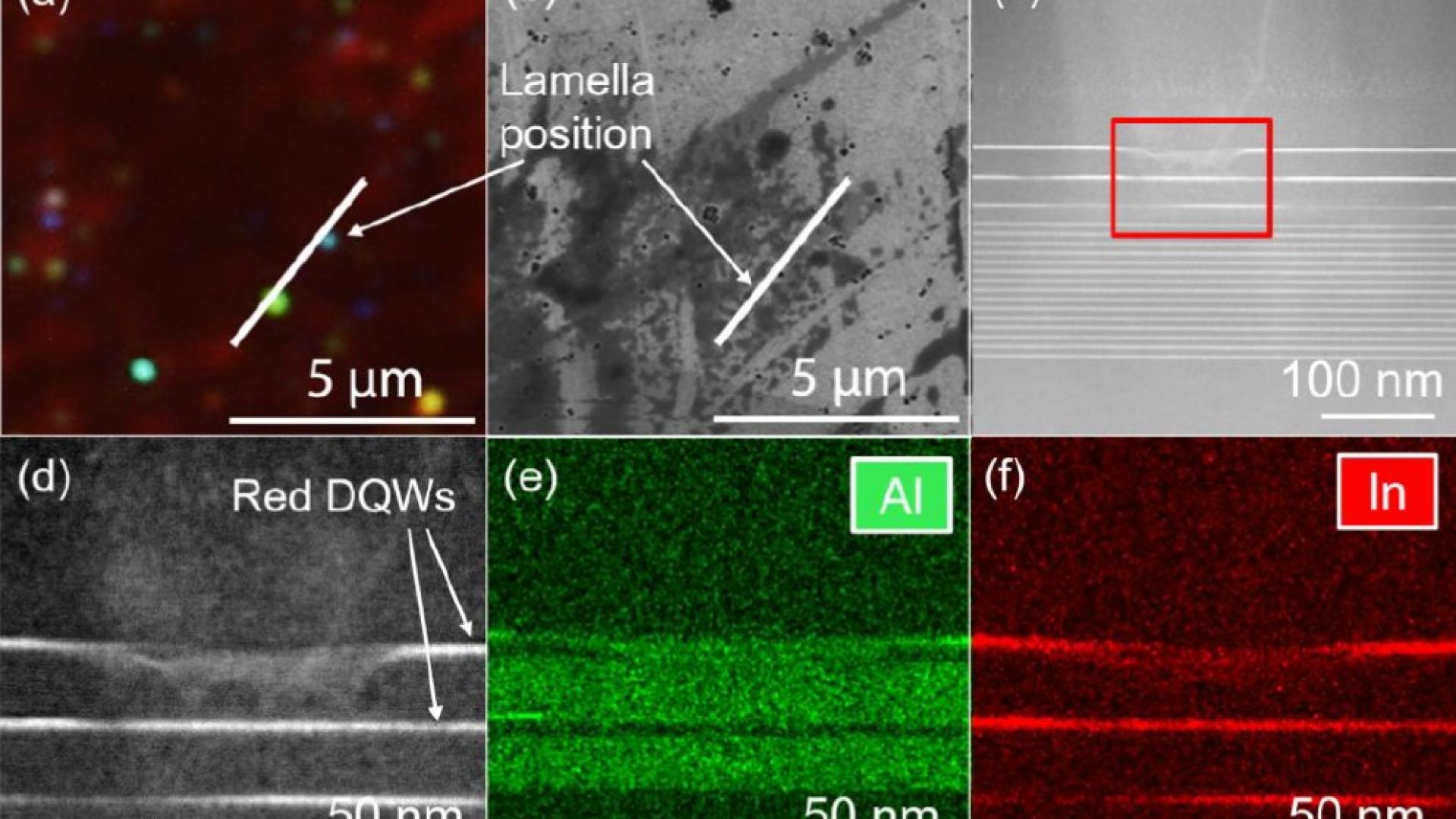
The paper reports the investigation of the electroluminescence properties of the additional peak in the EL spectrum of InGaN-based red LED structure. These results were helpful for understanding the EL performance of the red InGaN QWs and may be useful as guidelines to improve the quality of high-In-content QWs in the future.
Jin Yu is a physics graduate who joined KAUST in July 2021 from Nankai University (NKU), China. Before joining KAUST, Jin worked as an intern at Wake Forest University (WFU), North Carolina, U.S. After completing his studies at WFU, Jin served as a volunteer high school teacher at China Volunteer Association for almost a year.
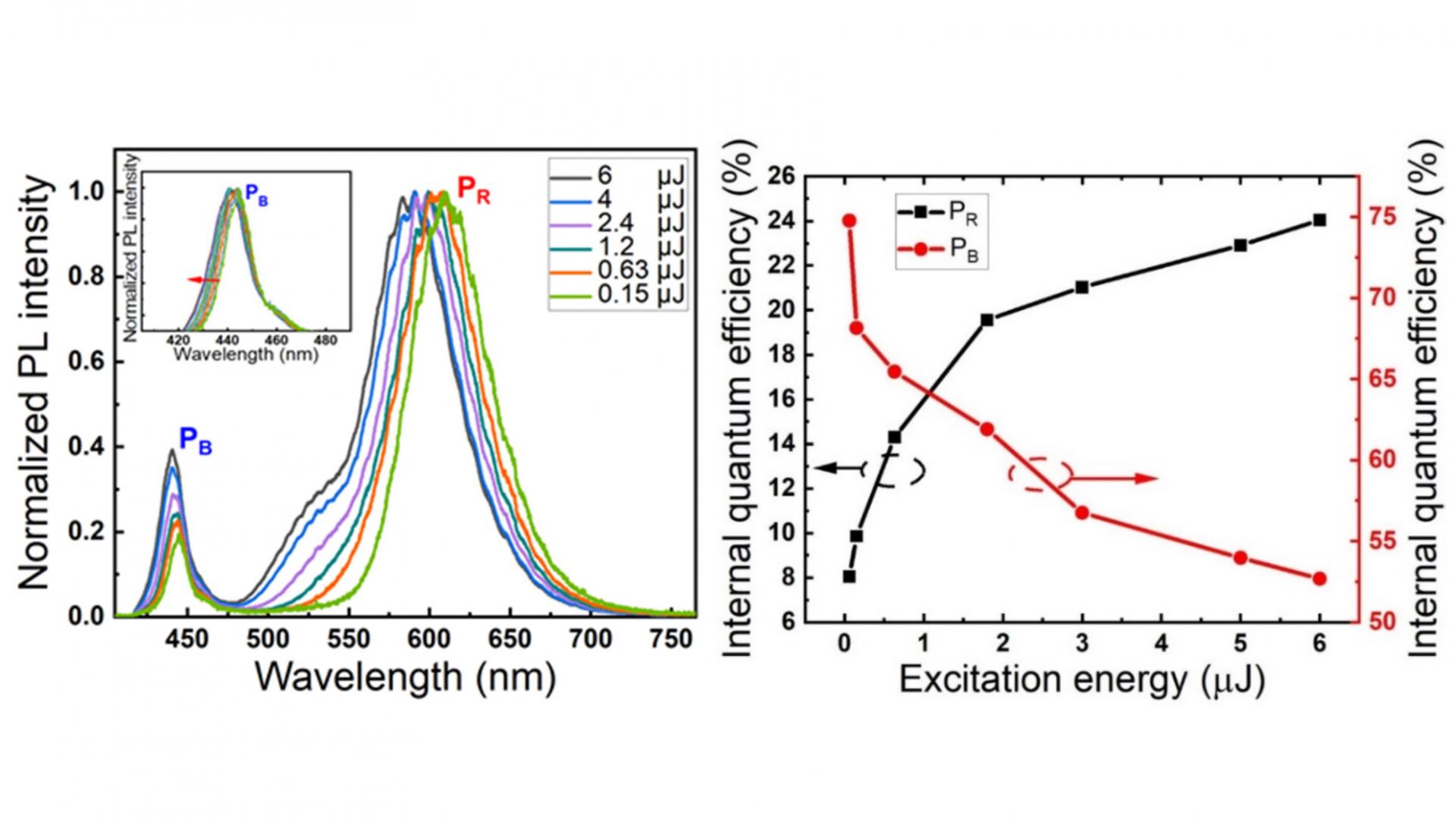
The paper reports the investigation of the optical properties of InGaN-based red LED structure with a blue pre-well by measuring the excitation energy and temperature dependent photoluminescence (PL) spectra. The deep localization of quasi-QD structures suppresses efficiently the escape of carriers and then enhances the emission in the red, which is the reason for strong emission intensity. The variation of internal quantum efficiency with excitation intensities indicates the better crystal quality of blue pre-well and the occurrence of defects in the red-emitting structures. The experimental results will provide a useful guidance to fabricate a longer wavelength InGaN-based optoelectronic devices with high-quantum efficiency.
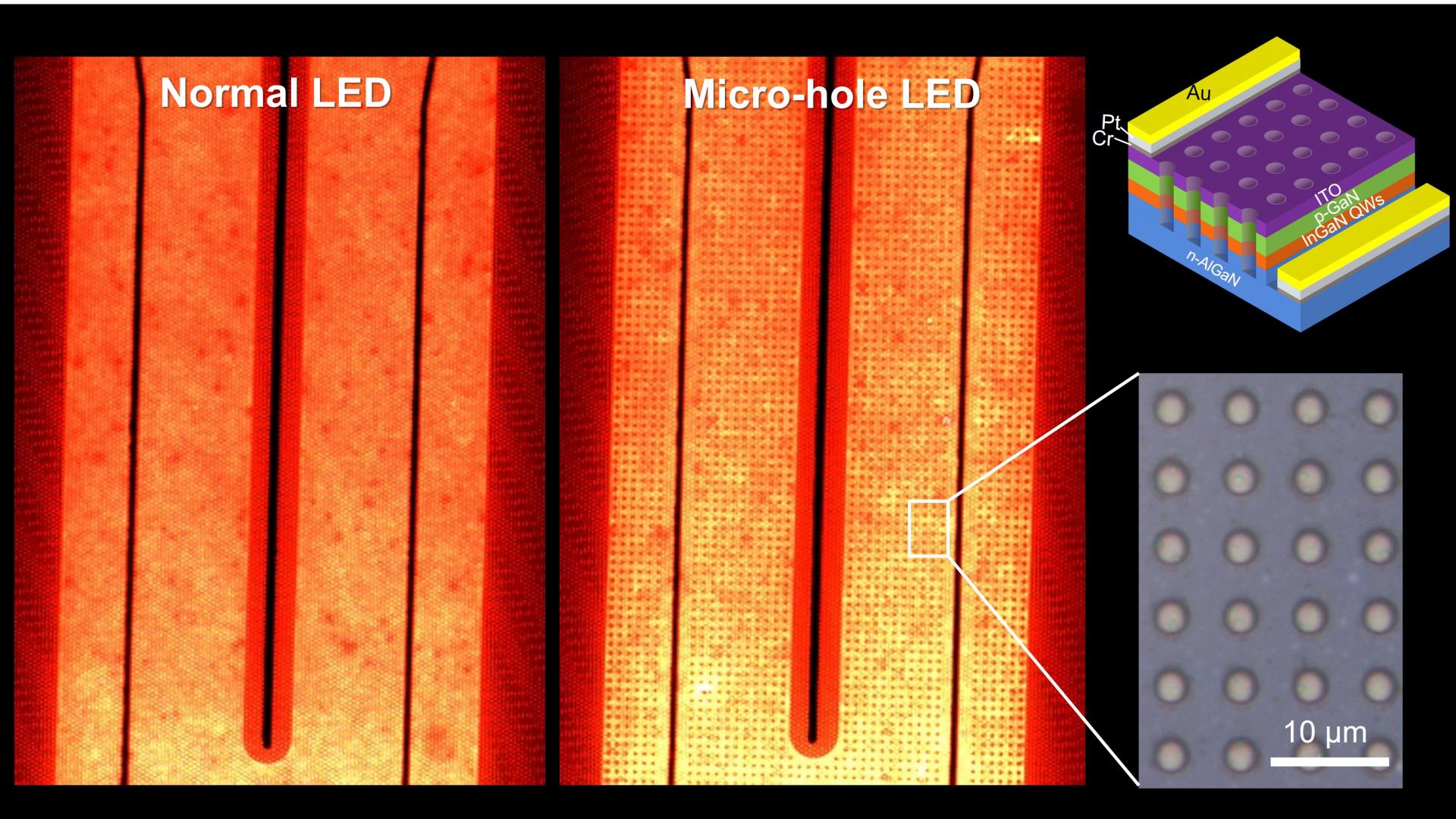
The paper reports the luminescence improvement of InGaN-based red LEDs by introducing a micro-hole array. This technique provides the improvement of the internal quantum efficiency and light extraction efficiency. The InGaN-based red LEDs are very attractive for next-generation micro-LED display, because the material is a family of blue and green LEDs.
The paper reports the new device fabrication for the green micro-LEDs. The micro-LEDs have recently gathered considerable interest for next-generation display applications, such as smartphones and watches, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) devices.
As one of the most cited articles from Saudi Arabia published across the entire IOP Publishing journal portfolio in 2020, using citations recorded in Web of Science
“Demonstration of low forward voltage InGaN-based red LEDs” D. Iida, Z. Zhuang, P. Kirilenko, M. Velazquez-Rizo, and K. Ohkawa, Applied Physics Express 13, 031001 (2020).
In this paper, we review our recent progress on InGaN-based red LEDs, including the epitaxial structures and device fabrication. We also present the optical performance of InGaN red LEDs with different chip sizes from hundreds to tens of micrometers.
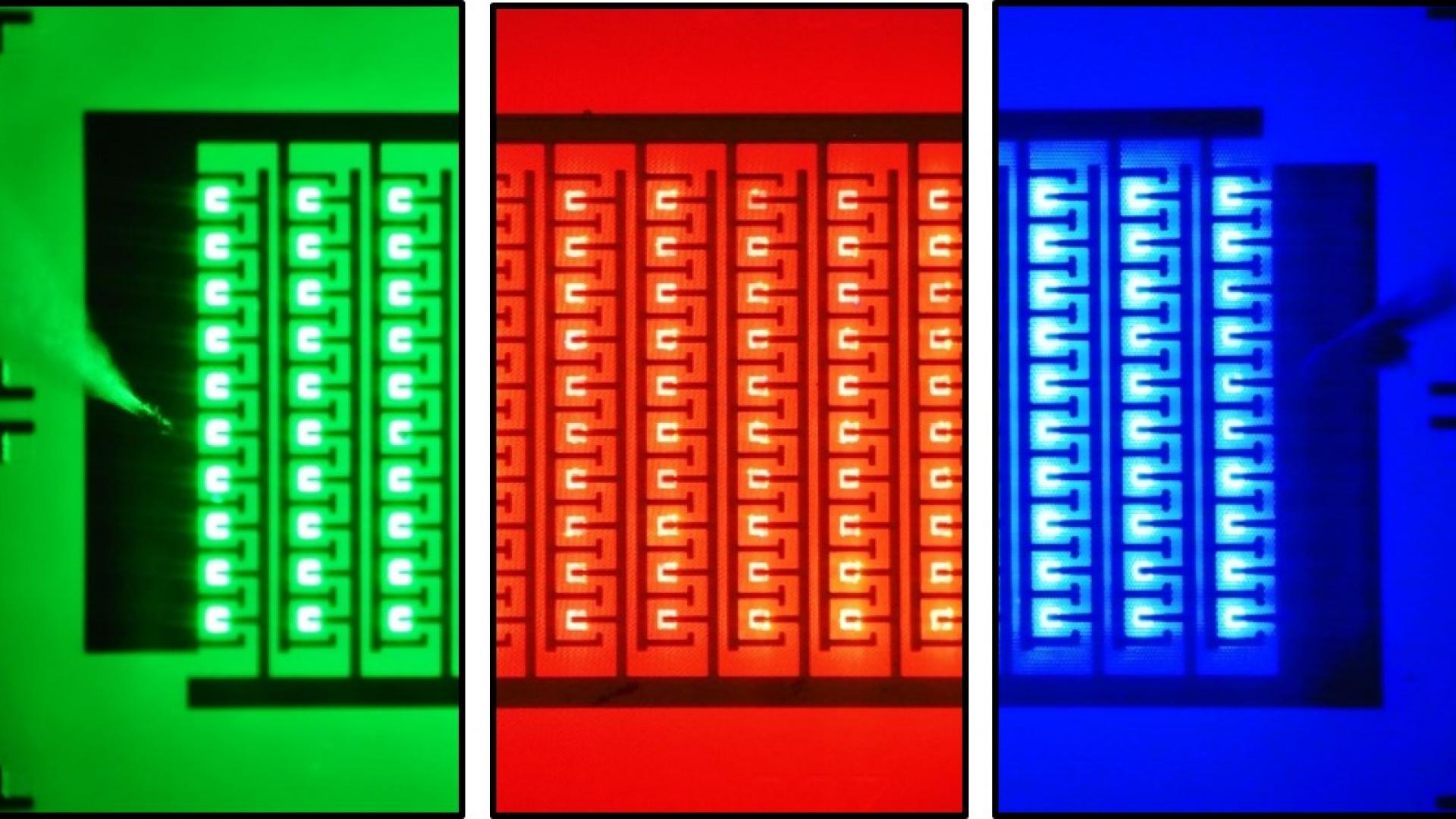
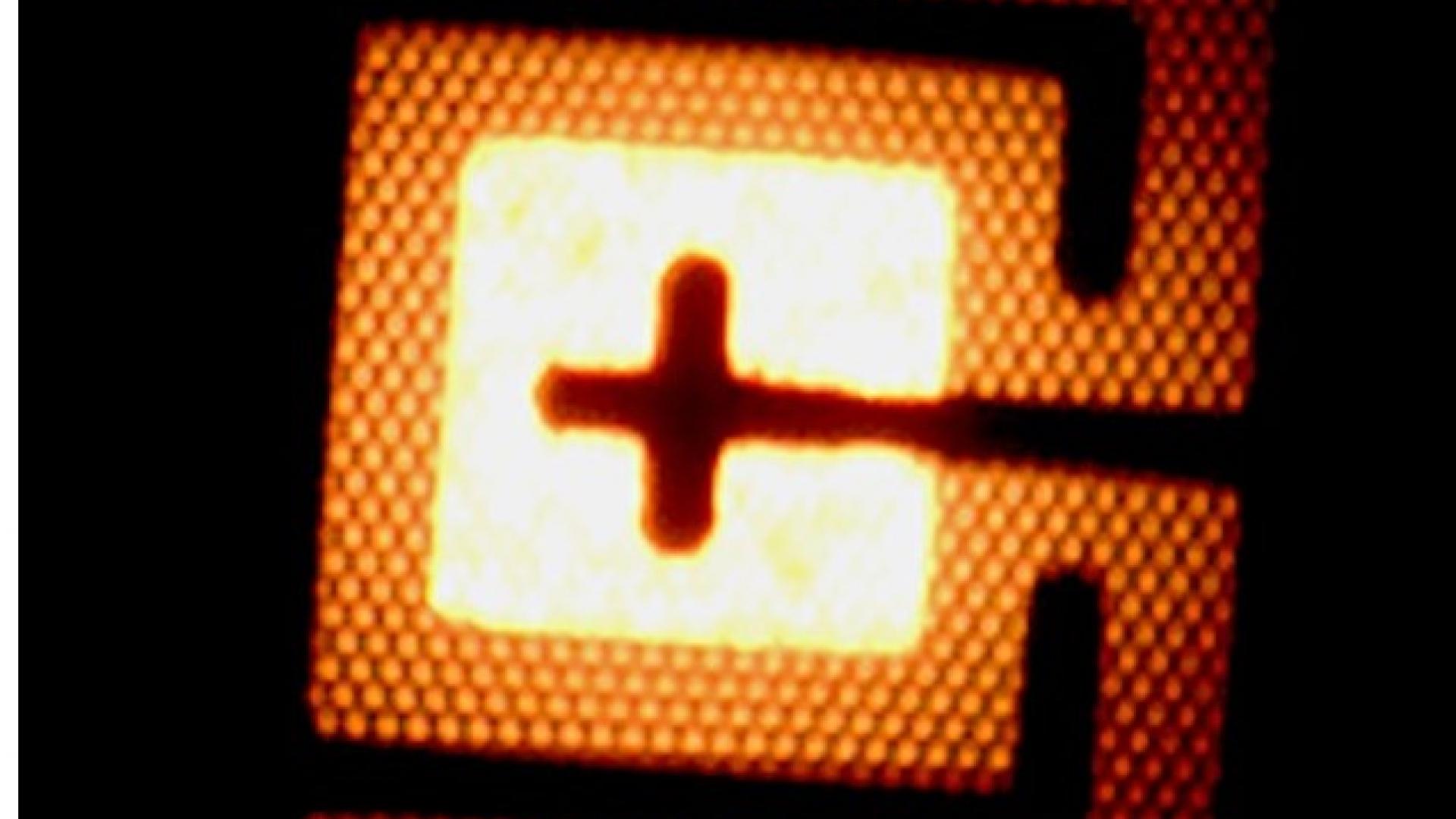
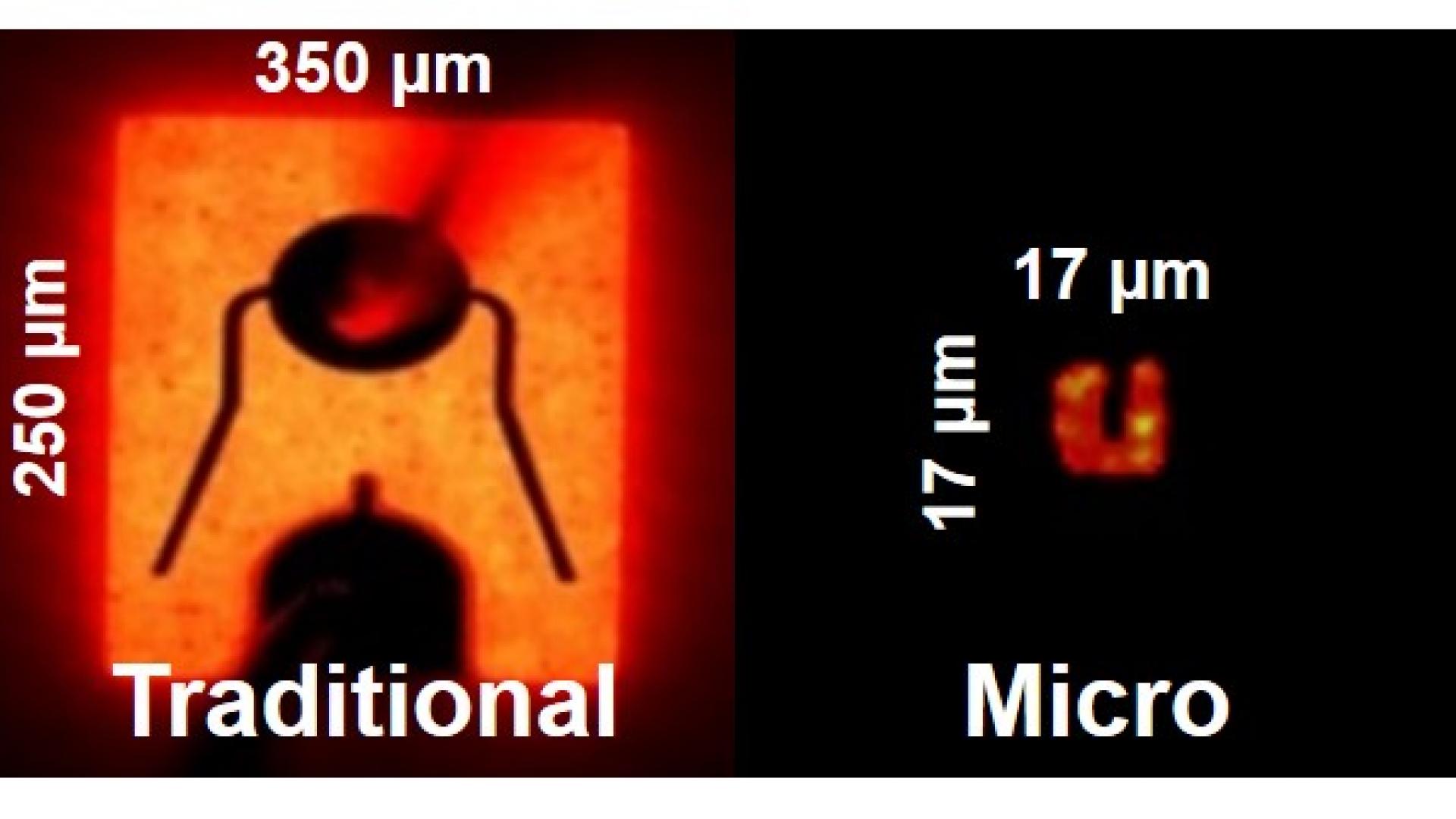
The paper reports InGaN-based RGB micro-LED arrays that comprise every single µLED in the dimension of 17 × 17 µm2. We obtained the output power density of the InGaN-based red µLEDs as 1.76 mW/mm2, which was estimated to be higher than that of 20 × 20 µm2 AlInGaP red µLEDs (~630 nm). The result reveals a great potential for the InGaN materials to be used in full-color micro-displays.
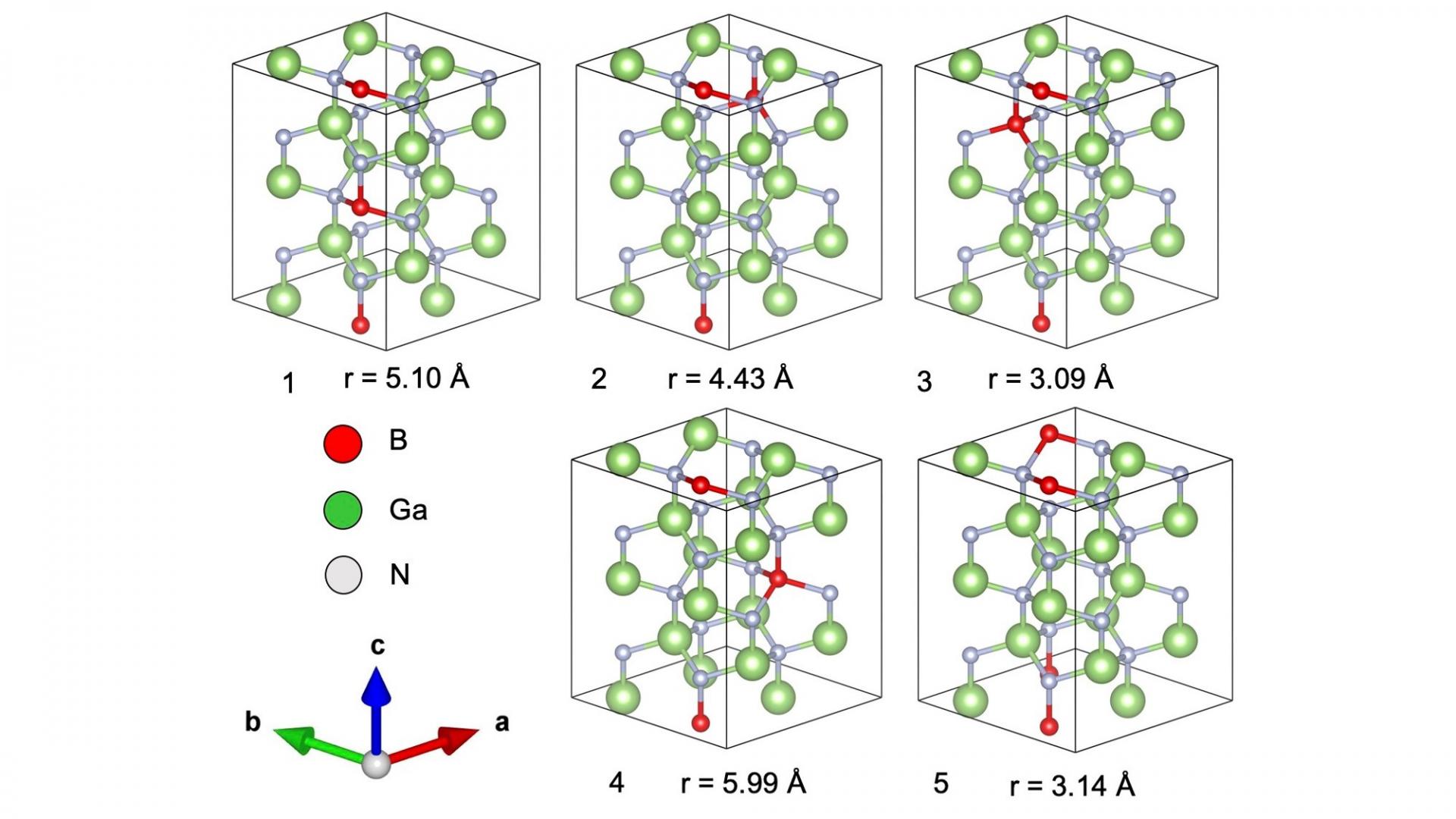
The paper reports an atomistic origin of composition pulling effect in all GaN-based ternary alloy was clarified from the the geometric configurations using first-principles calculations. We found that the most stable configuration involves two B, In, or Al atoms occupying Ga sites in wurtzite GaN along the c-axis which is the typical epitaxial growth direction.
606-nm InGaN Amber Micro-Light-Emitting Diodes With an On-Wafer External Quantum Efficiency of 0.56%
The paper reports the device performances of the amber micro-LEDs. The on-wafer external quantum efficiency was as high as 0.56%. The micro-LEDs have recently gathered considerable interest for next-generation display applications, such as smartphones and watches, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) devices.