
Research at the Organic Bioelectronics Laboratory focuses on coupling of organic electronic materials with biological systems. Their aim is to develop electronic devices that can interface with living systems and detect or treat diseases in ways that have not been possible before. These devices might include an implant that goes into the heart and regulates the heartbeat or when placed in the brain, via delivery of drugs or electrical stimulation, alleviates symptoms of a neurological disorder. They can as well pick up biological signals and translate these into electrical information, forming the basis of a biosensor. The success of these devices, however, depends on how well the electronics communicate with the biological system. And materials that enable communication between these two worlds are the key to building high-performance devices.
In the lab, they employ organic electronic materials, that are carbon-based semiconductors, for interfacing the living tissue. Sharing similar building blocks with living organisms, these materials bring together a unique set of properties that can be leveraged to improve the compatibility of artificial devices. For instance, they soften up as they interact with the body fluid, dampening the mechanical mismatch with the tissue. They transport electronic charges like metals but are also ionically active like biological systems. As such, organic electronic materials provide a new toolbox for interfacing with biology. Leveraging the properties of organic electronic materials, their goal is to design bio-sensing and stimulation platforms with unique capabilities.
The Laboratory has several state of the art facilities and equipment’s. Some of them are listed below:
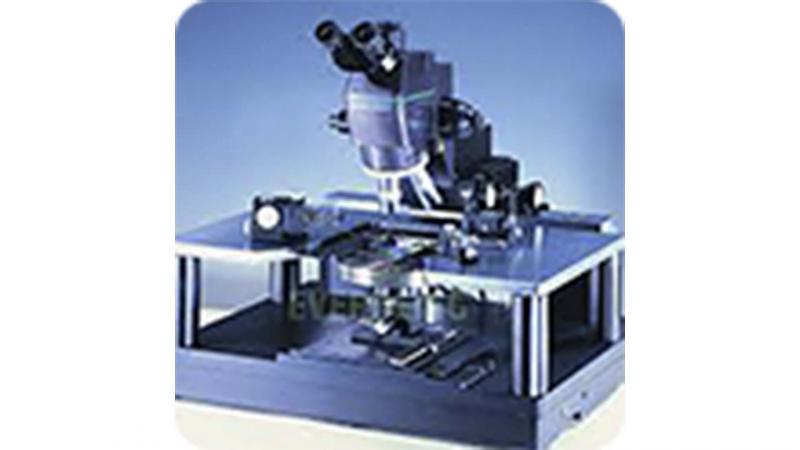

Probe Station
Probe station (equipped with source-measure units such as a Keithley or a National Instruments System) enables electrical characterization of materials and devices. Read more...
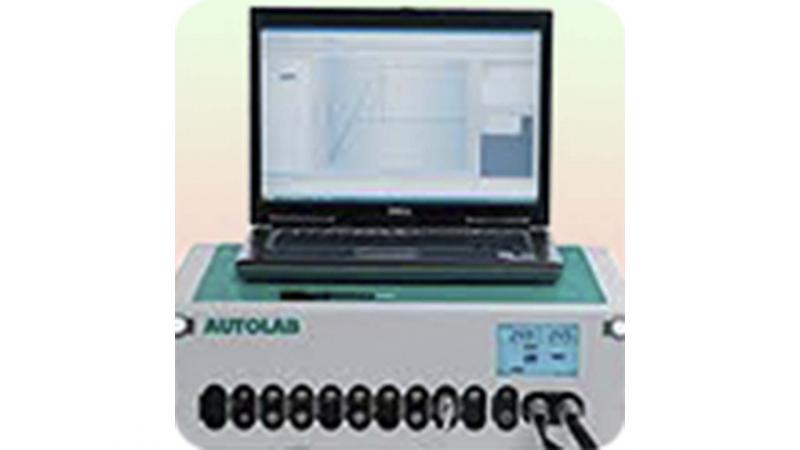

Potentiostat/galvanostat
The instrument is a used for a wide range of applications, including electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry etc. Read more..
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D)
The QCM-D is a powerful instrument that can quantify surface interactions/reactions in real time. Read more...
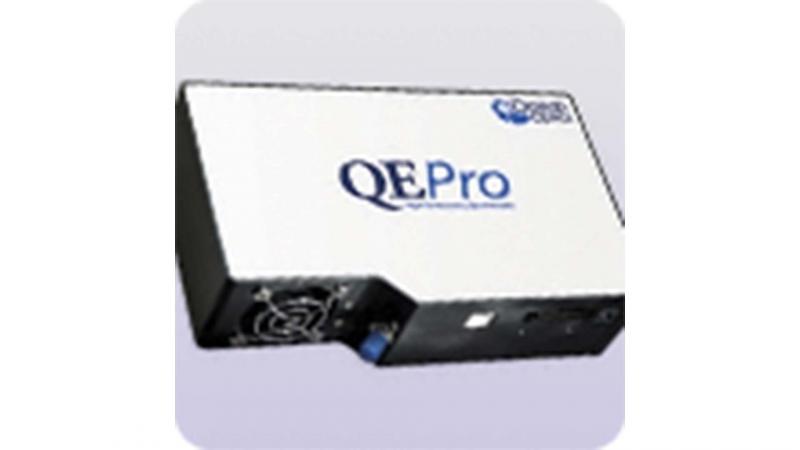

VIS-NIR fiber optics spectrometer with halogen lamp
The spectrometer measures the visible spectrum of samples up to 1200 nm, as well as fluorescence signals in the visible range. Read more...
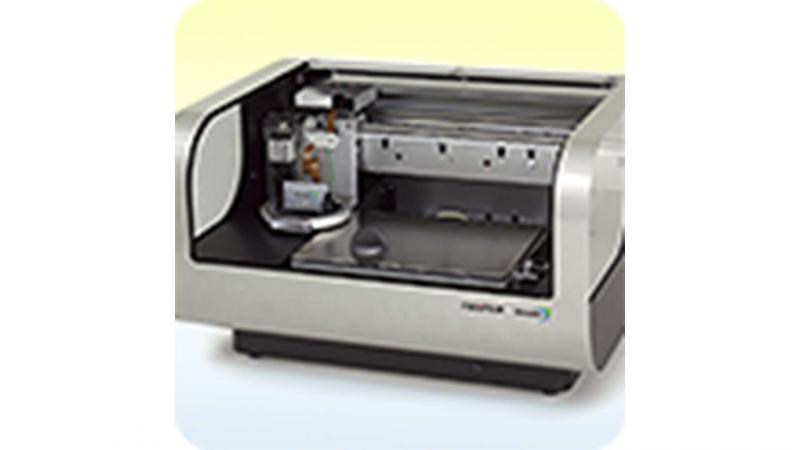

Inkjet Printer
The inkjet printer is used to print various materials, including conducting polymers such as PEDOT:PSS, on a variety of substrates (e.g., textile, glass, parylene).
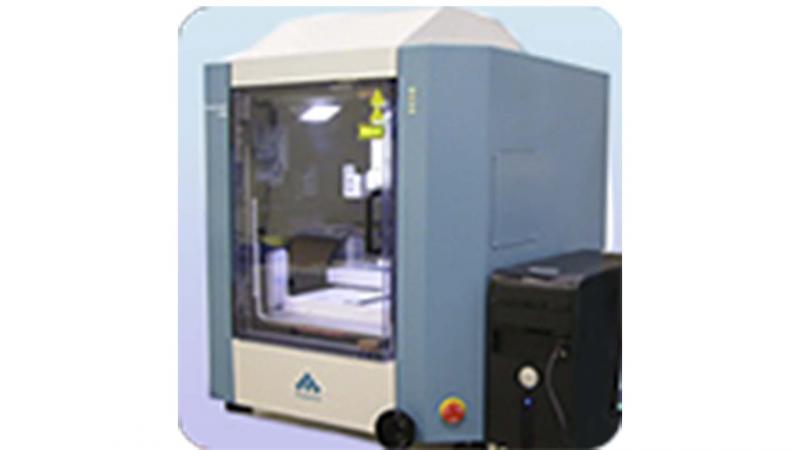

Electrospinner
Electrospinner/sprayer fabricates polymeric nanofibers, using electrostatic force that transforms charged threads of polymer solutions into fibers.
For more information please visit Organic Bioelectronics Laboratory website bioel.kaust.edu.sa.